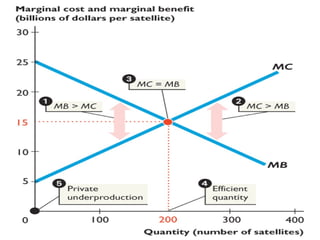
The free-rider problem occurs when individuals receive benefits from a public good without contributing to its provision. This leads to an underprovision of public goods, as individuals have no incentive to pay for something they can access without paying. Public provision of goods can overcome this by requiring contributions through taxes that are used to fund public goods from which all benefit.