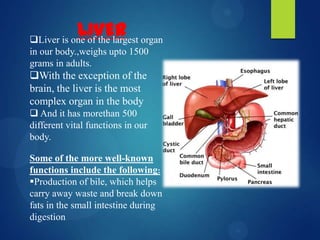
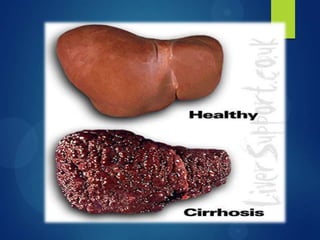
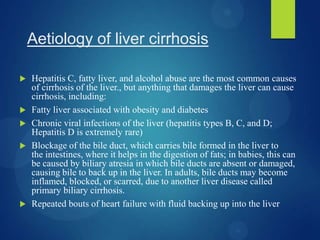
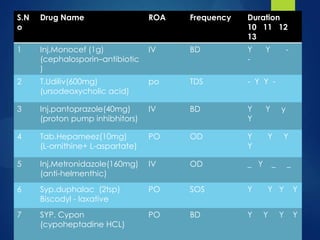
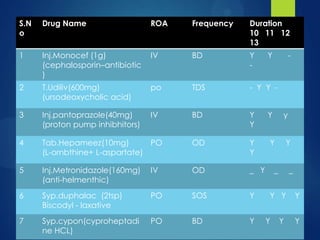
This case study describes a 70-year-old male patient admitted to the hospital with abdominal distention, weakness, decreased appetite, and weight loss. His medical history revealed he was an alcoholic and smoker. Diagnostic tests showed signs of liver damage. Alcoholic liver cirrhosis occurs in stages from fatty liver to inflammation and scarring of the liver. Risk factors include quantity of alcohol consumed, genetics, and malnutrition. Treatment requires stopping alcohol consumption and may include vitamins, diet, and transplantation for severe cases.