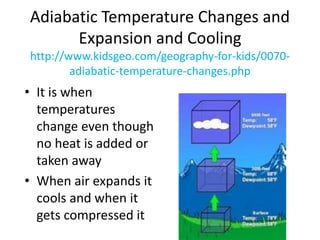
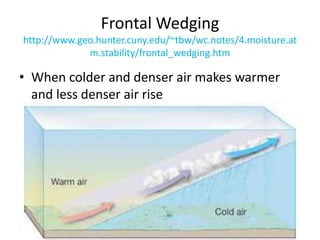
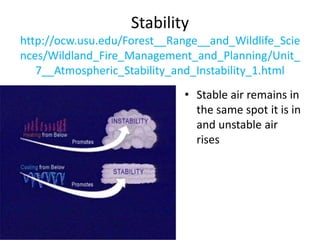
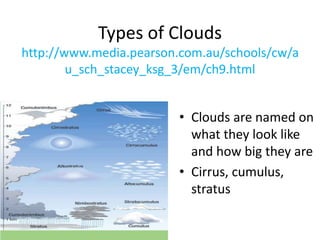
The document discusses various cloud formation processes including adiabatic cooling, orographic lifting, frontal wedging, convergence, and localized convective lifting. It describes cloud types such as cirrus, cumulus, and stratus clouds and how they are classified by appearance and size. The document also covers precipitation processes for warm and cold clouds, types of precipitation including rain, snow, sleet, glaze and hail, and fog formation.