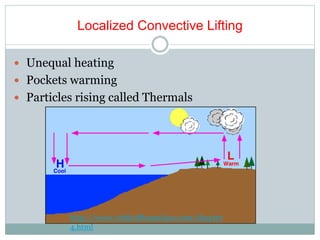
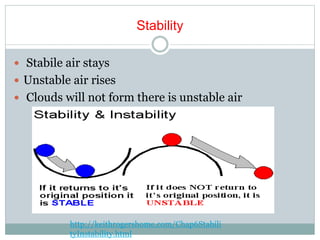
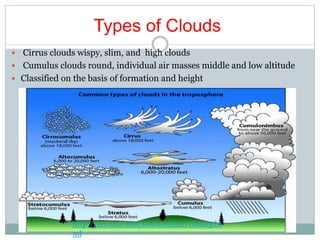
This document discusses various cloud and precipitation formation processes. It begins by explaining adiabatic temperature changes and how they relate to cloud development. It then discusses orographic lifting, convergence, localized convective lifting, stability, and condensation - all of which can induce clouds and precipitation. The document also classifies common cloud types such as cirrus, cumulus, and stratus clouds. It concludes by examining different types of precipitation including rain, snow, sleet, glaze and hail.