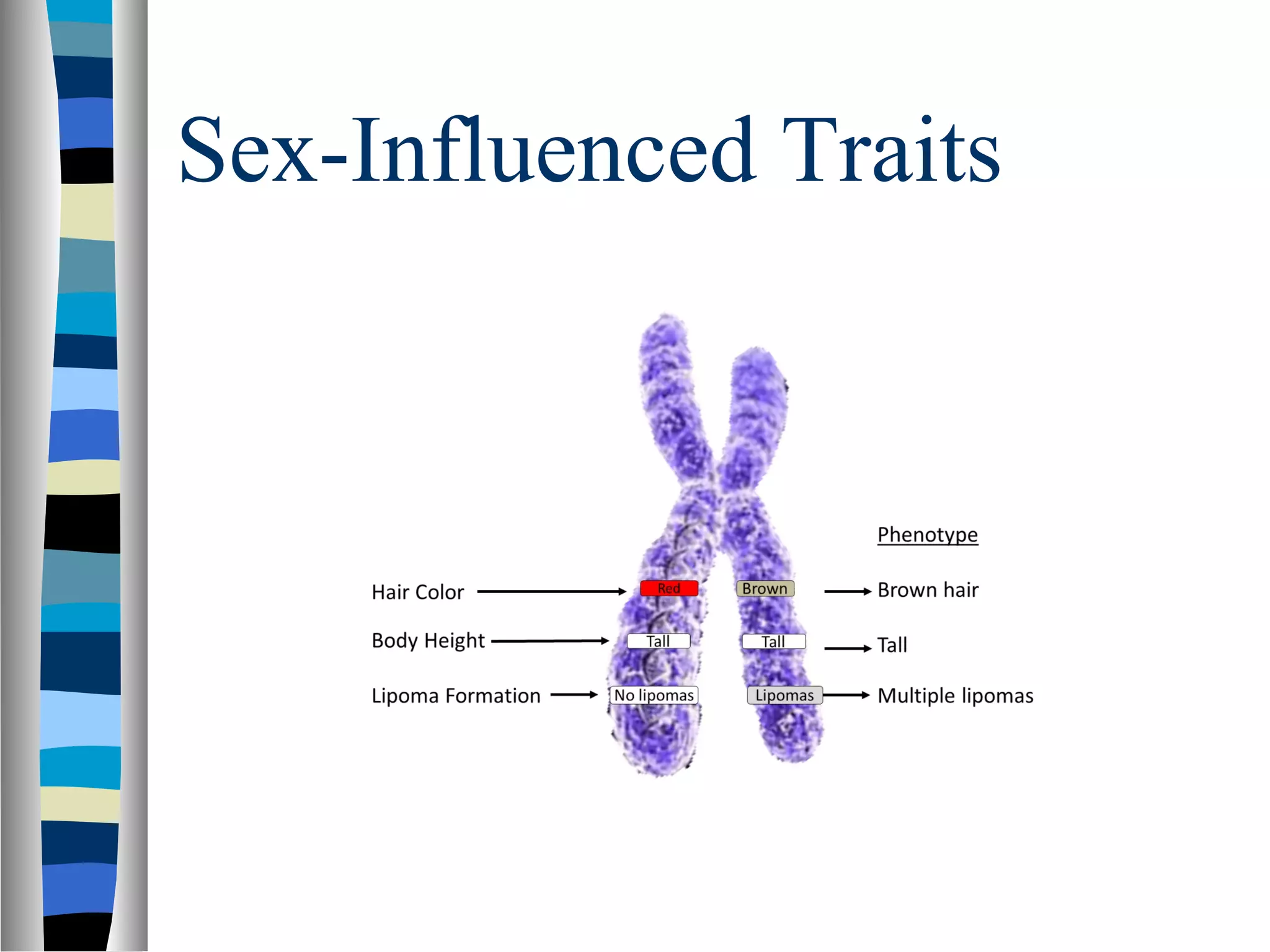
The document discusses sex-influenced traits, which are traits controlled by alleles on autosomal chromosomes, with their expression influenced by hormones like testosterone. An example is pattern baldness, more common in males due to the dominant nature of the baldness allele in the presence of high testosterone levels. It also details genetic terms such as heterozygous and homozygous, explaining how different genotypes can result in varying phenotypic expressions based on sex.