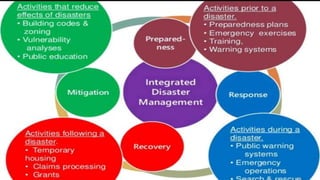
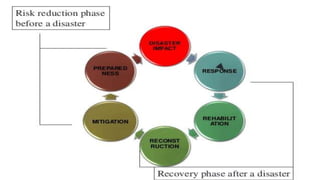
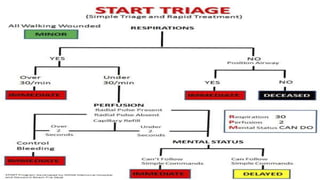
This document provides information on disaster management and triage. It defines a disaster as an event that exceeds the normal capacity for adjustment. Disasters are classified based on cause (natural vs man-made) and location (out-of-hospital vs in-hospital). The key phases of disaster management are preparedness, impact, response and rescue, and recovery. Triage involves sorting patients into categories based on severity using approaches like SALT (sort, assess, life-saving interventions, transport) to prioritize treatment. Major international agencies that assist with disaster management include the United Nations, Red Cross, World Bank, and European Union.