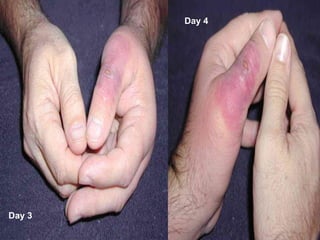
The document provides comprehensive guidelines for basic first aid, emphasizing the importance of securing the scene, understanding the chain of survival, and universal precautions for preventing disease transmission. Key topics include assessing and treating various injuries, performing CPR, controlling bleeding, and recognizing signs of shock and heat emergencies. It also highlights specific treatments for burns, diabetic emergencies, bites, fractures, and the importance of proper care while waiting for emergency services.