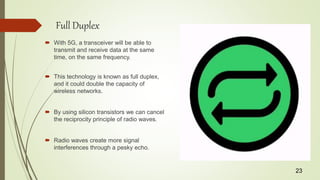
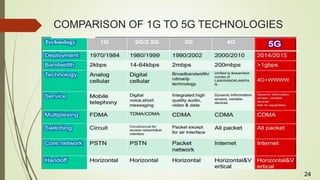
The document discusses the evolution of mobile network technologies from 1G to 5G. It provides details on the key features and technologies of each generation including network speeds, capabilities and limitations. 5G is described as being able to provide speeds up to 1Gbps using technologies like millimeter waves, small cells, massive MIMO, beamforming and full duplex to help address limitations of previous standards like inability to handle high speeds or pass through obstacles. 5G is predicted to deliver enhanced mobile broadband and help enable new applications.