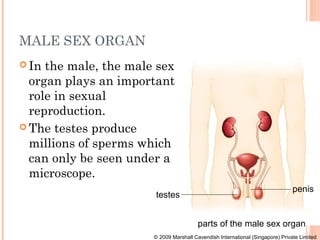
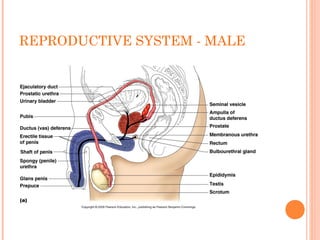
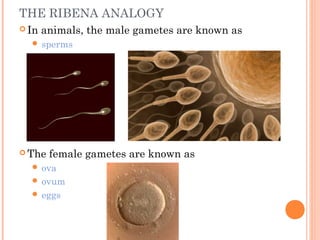
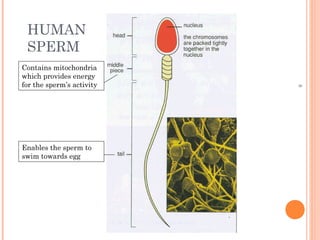
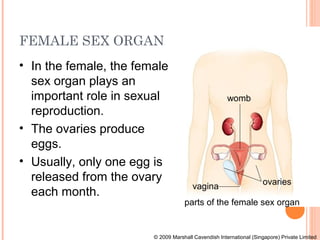
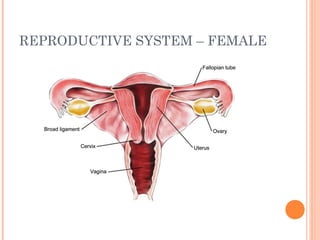
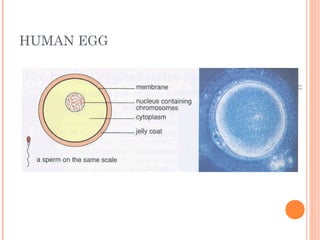
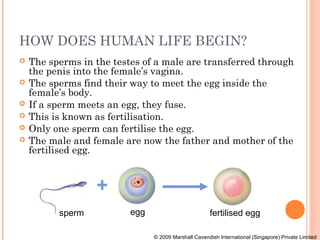
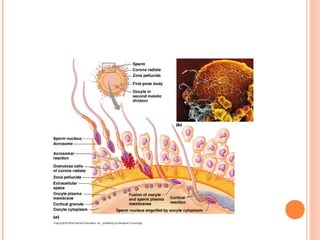
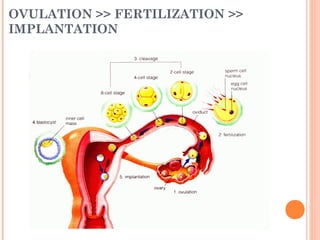
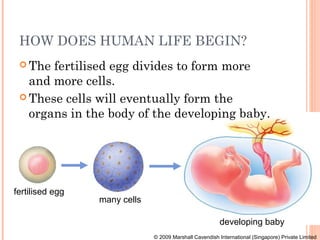
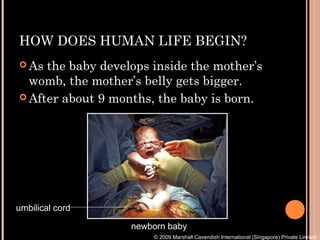
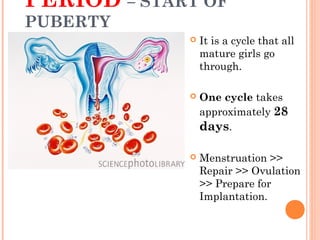
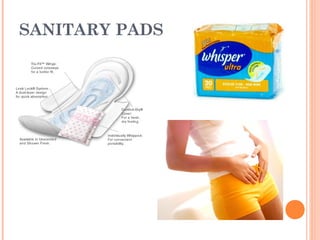
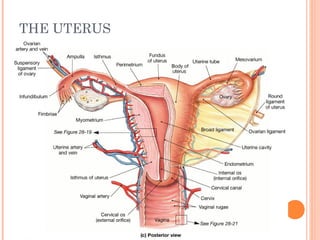
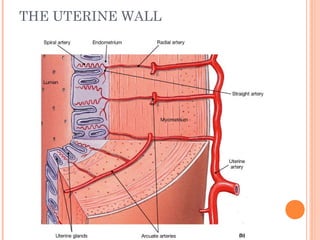
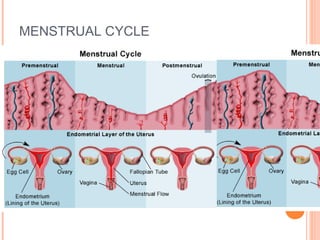
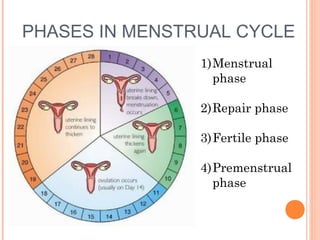
The document summarizes the human reproductive system and process of reproduction. It describes that males have testes that produce sperm and a penis, while females have ovaries that produce eggs and a uterus. Fertilization occurs when a sperm penetrates an egg in the female's ovaries or fallopian tubes. The fertilized egg then implants in the uterus and develops into a fetus over 9 months of pregnancy before birth. Key parts of both the male and female reproductive systems and stages of fertilization, pregnancy, and birth are outlined.