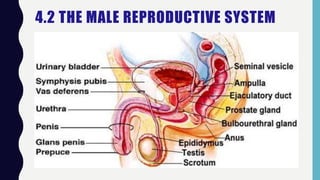
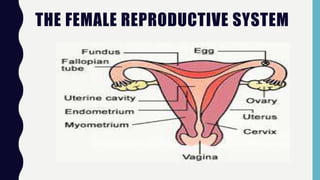
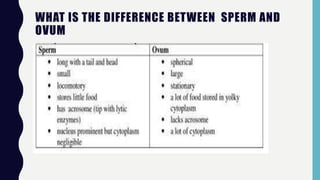
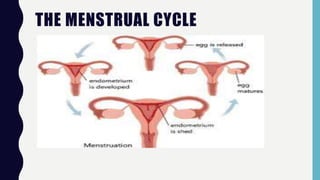
This document discusses sexual and asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction involves two parents and the fusion of gametes through fertilization, resulting in offspring with genetic variations. Asexual reproduction involves one parent and occurs through processes like budding, spore formation, or regeneration, where offspring are identical to the parent. The document also describes the male and female human reproductive systems and stages of the menstrual cycle. Different methods of human birth control like condoms, pills, and IUDs are explained. The process of pollination and conditions for seed germination are outlined.