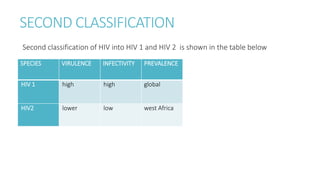
The document discusses HIV classification, structure, pathogenesis, and modes of transmission. It describes the CDC classification system for HIV based on CD4 cell counts and conditions, with categories A, B, and C. It explains HIV's structure including its envelope, matrix proteins, core, and RNA. HIV pathogenesis involves binding to and fusing with host cells, reverse transcribing its RNA into DNA, and using the host cell to replicate. HIV is typically transmitted via unprotected sex, contaminated needles, or from mother to child during birth or breastfeeding.