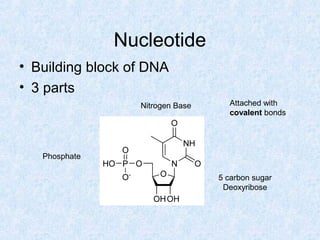
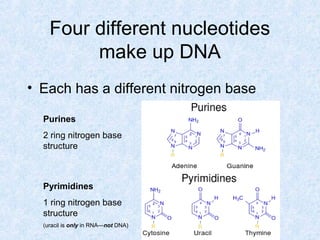
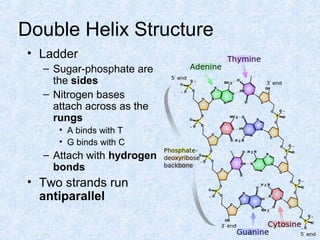
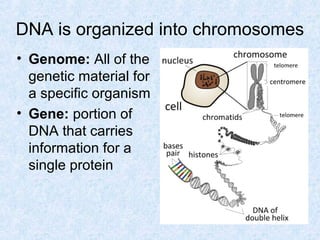
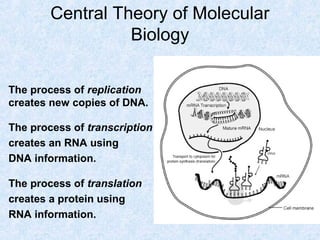
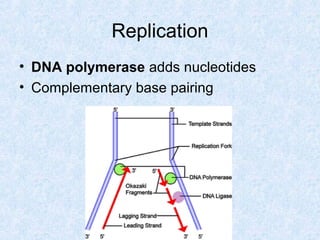
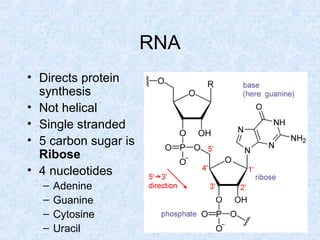
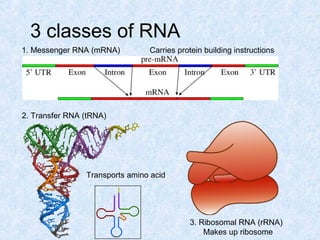
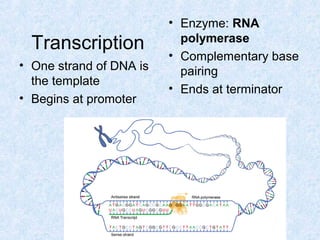
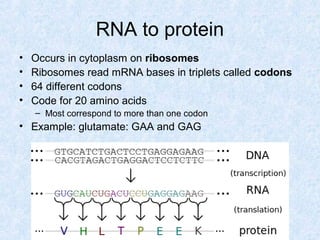
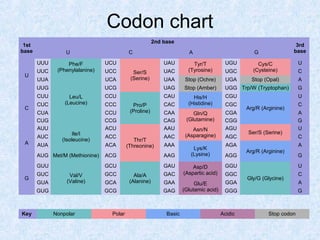
DNA is the chemical compound that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all living organisms. It is found within the nuclei of cells. DNA is composed of nucleotides, which contain phosphate, sugar, and a nitrogenous base. The four nucleotides are attached via covalent bonds to form two strands that twist into a double helix structure. DNA is organized into structures called chromosomes within the cell nucleus. It replicates via semi-conservative replication and uses transcription and translation to synthesize proteins. RNA assists in protein production by carrying protein building instructions from DNA to the ribosomes.