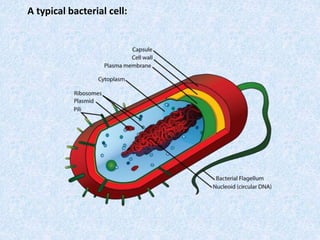
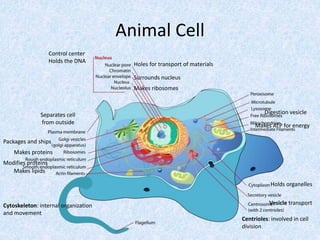
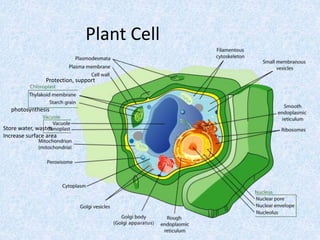
Cells are the smallest and most basic unit of life. There are two main types of cells - prokaryotic cells which are simple and lack organelles, and eukaryotic cells which are more complex and contain organelles. Eukaryotic cells include animal and plant cells which have internal structures like a nucleus that holds DNA, organelles for functions like protein production, and a cytoskeleton for internal organization and movement.