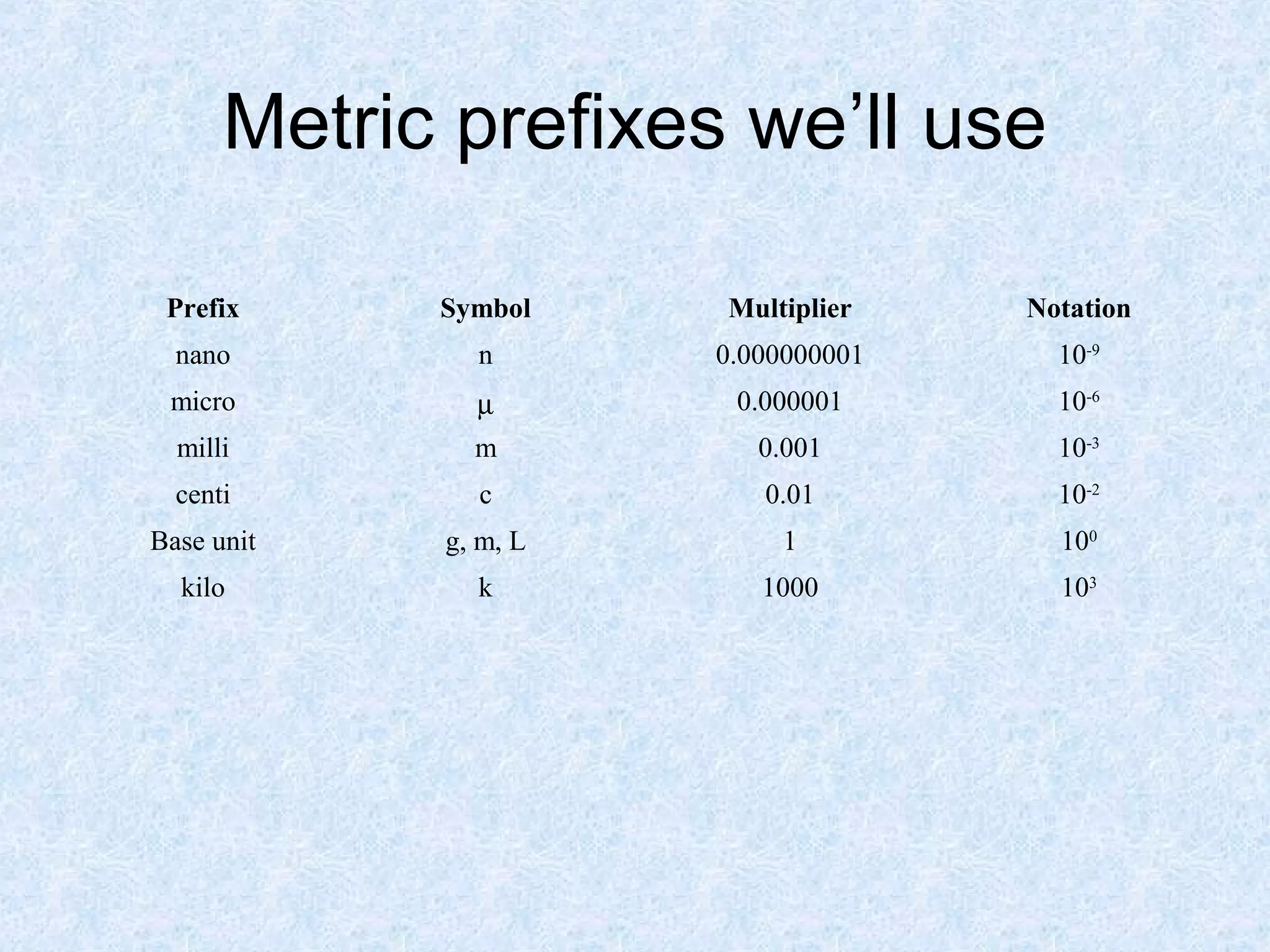
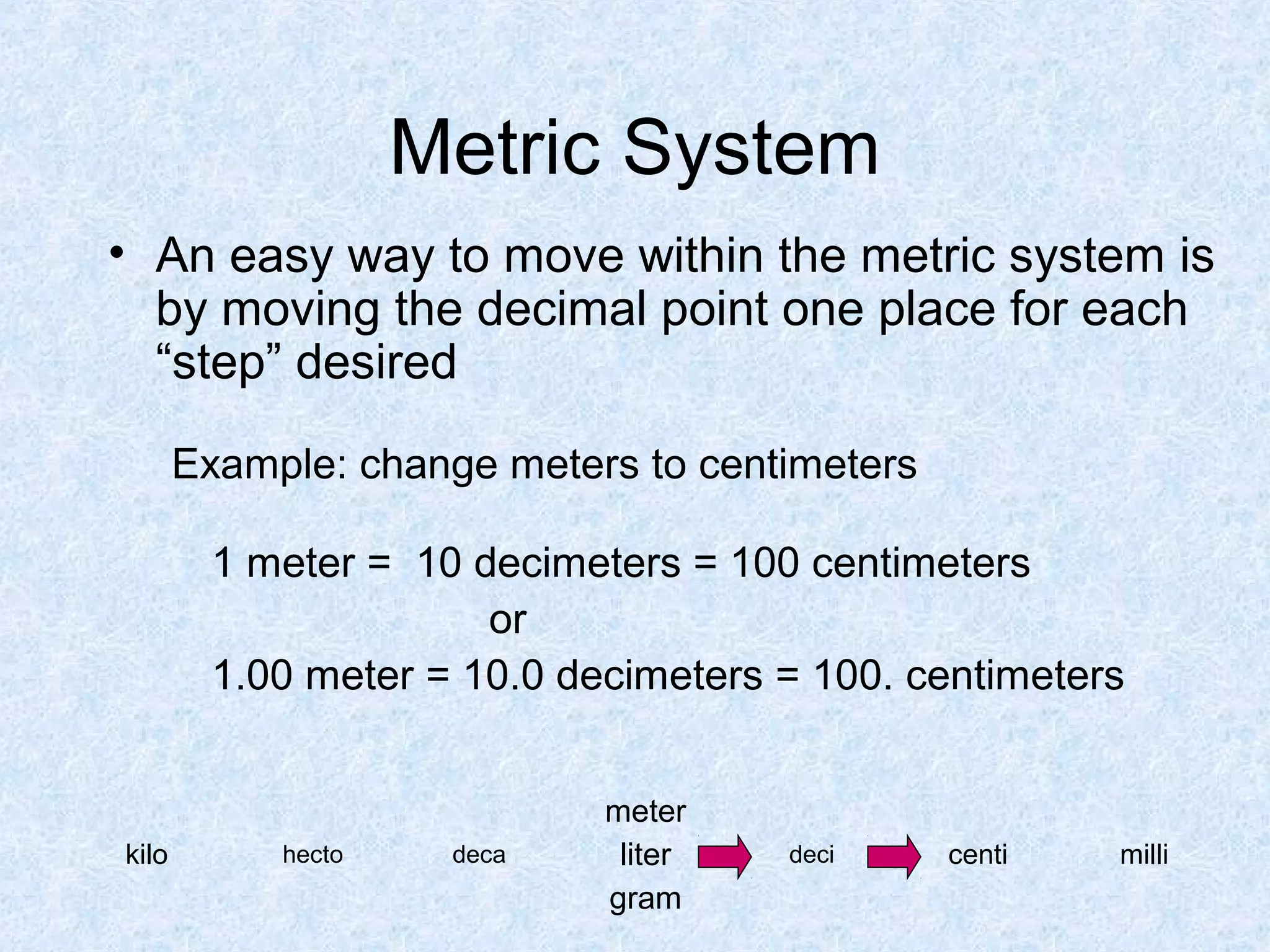
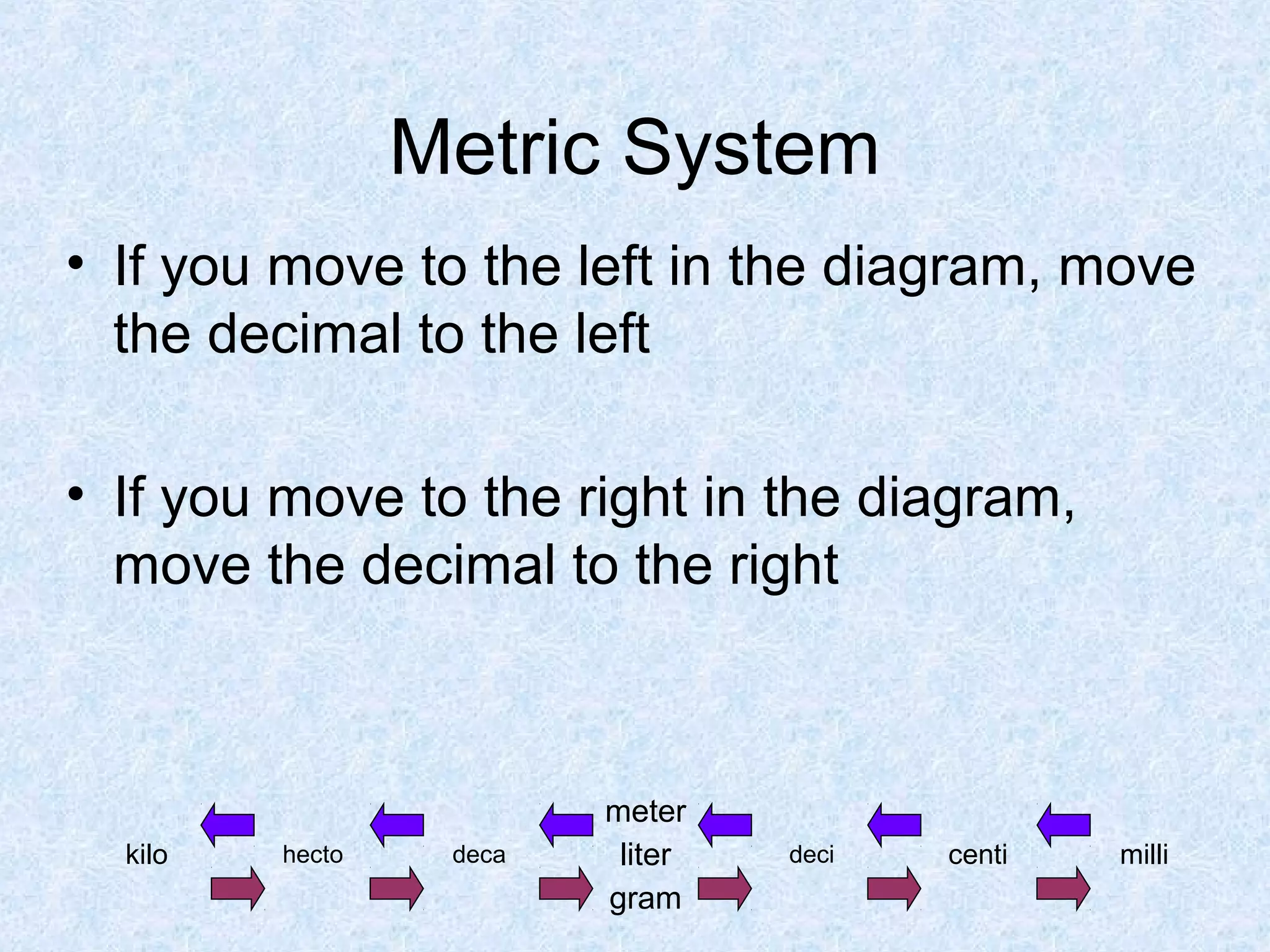
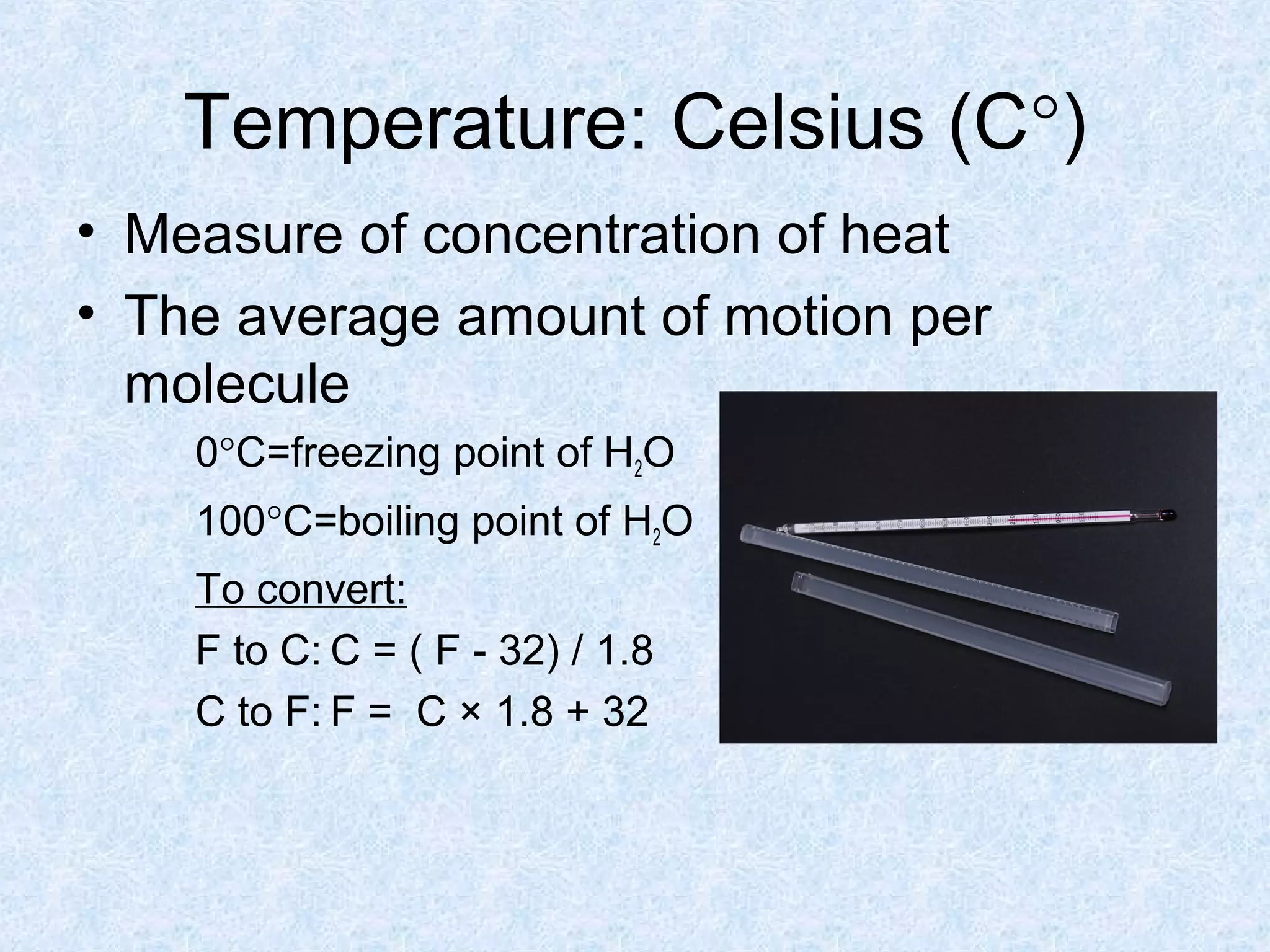
The metric system was devised in 1791 by the French Academy of Sciences to create a standardized system of measurement. It uses a base-10 system and standardized units like meters, liters, and grams that are related by powers of 10. Conversions between units are easy by moving the decimal point a place for each power of 10. The metric system was widely adopted and later renamed the International System of Units. It provides standardized units and prefixes to measure length, volume, mass, and temperature.