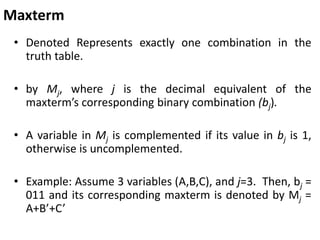
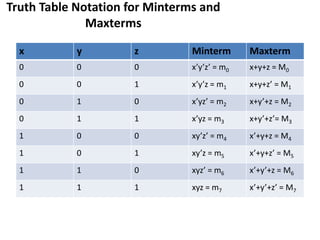
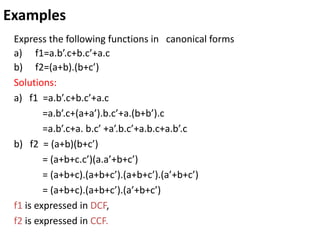
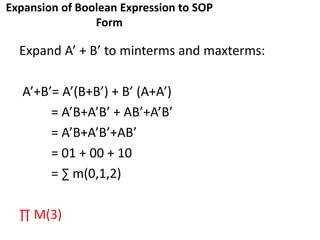
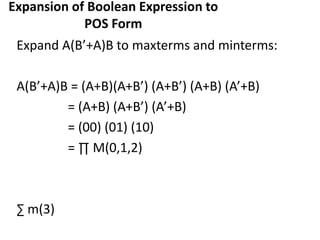
The document discusses Boolean functions and their representation in normal forms. It defines key concepts such as literals, product terms, sum terms, sum of products (SOP) form, product of sums (POS) form, standard form, non-standard form, minterms, maxterms, canonical form, conversion between forms, and shorthand notation using Σ and Π. Examples are provided to illustrate Boolean expressions in SOP and POS forms, their expansion to minterms and maxterms, and conversion between standard and canonical forms.