1. Acids donate H+ ions in solution while bases accept H+ ions, helping to regulate pH.
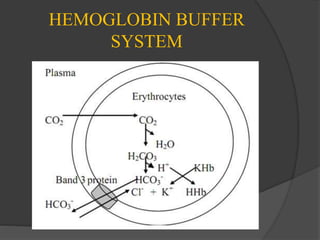
2. The bicarbonate buffer system, hemoglobin buffer system, and phosphate buffers help maintain acid-base balance by absorbing excess H+ ions.
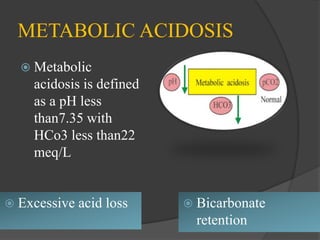
3. Imbalances can occur from respiratory or metabolic causes and are diagnosed based on blood pH and bicarbonate levels, with treatment focusing on the underlying condition and restoring normal acid-base levels.