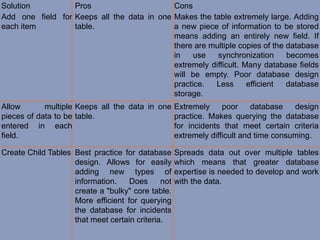
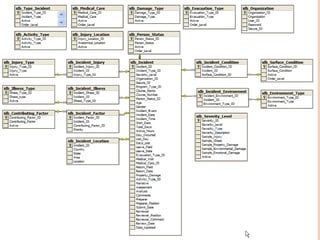
The document discusses database design and the design process. It explains that database design involves determining the relationships between data elements, structuring them logically, and specifying attributes. The design process includes determining the database purpose, finding and organizing information, dividing it into tables, specifying columns and primary keys, and setting up relationships. It also recommends creating child tables to store multiple pieces of information rather than adding many fields to the core table. This improves the database structure and makes it more extensible.