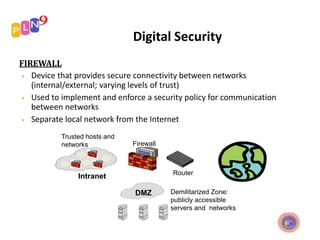
Physical security involves protecting assets and information from unauthorized physical access through methods like locking doors, securing documents, using biometrics like fingerprints, ID badges, key fobs, and RFID cards. Digital security focuses on preventing harmful data and malware through antivirus software, firewalls, antispyware, and enforcing strong passwords and directory permissions. Both physical and digital security are important parts of an organization's complete security solution.