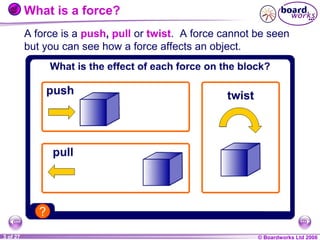
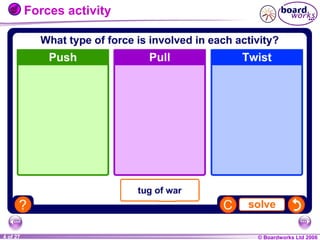
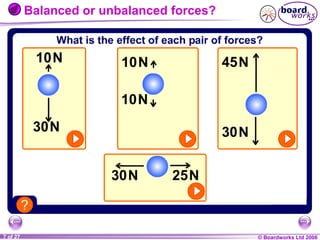
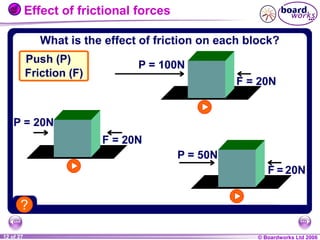
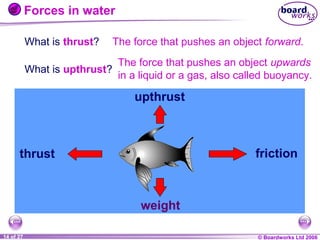
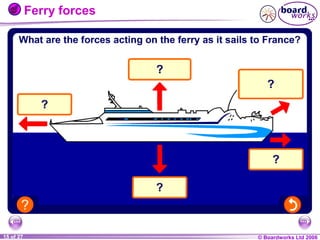
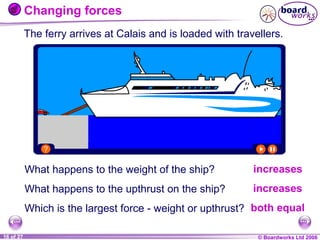
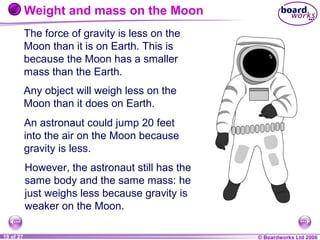
The document is a physics textbook section about forces and their effects. It contains multiple pages explaining key concepts such as what forces are, how balanced and unbalanced forces affect motion, the different types of forces like friction and gravity, and the difference between mass and weight. Diagrams and activities are provided to illustrate these concepts.