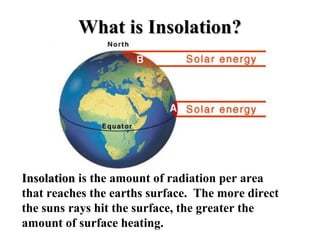
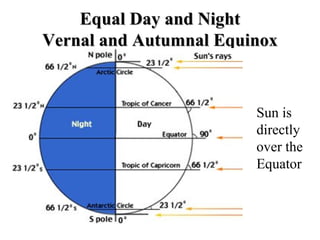
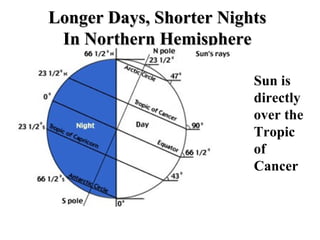
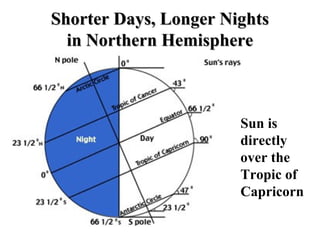
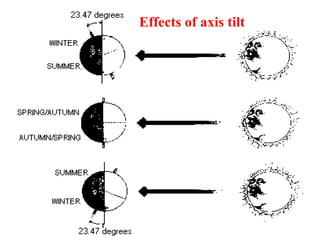
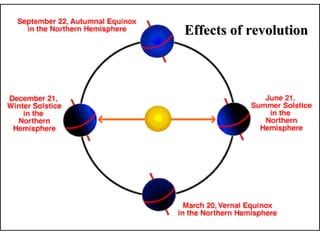
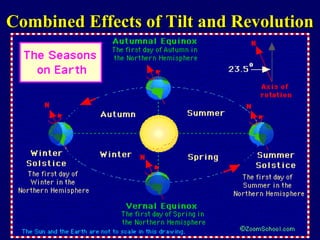
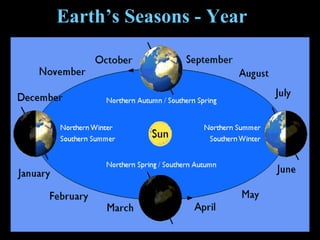
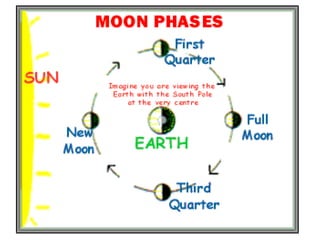
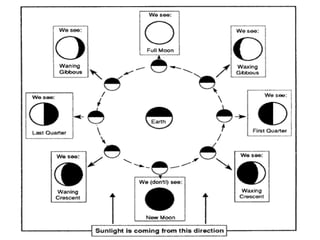
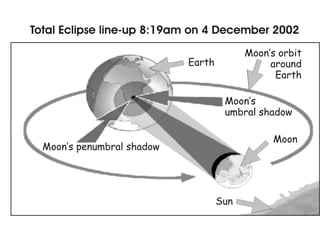
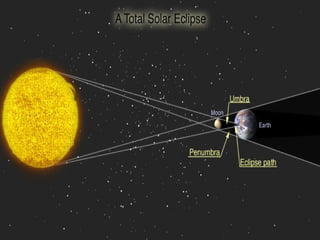
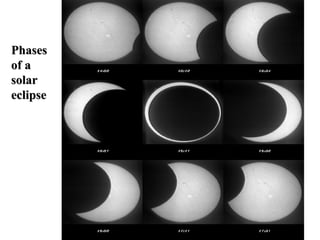
The document discusses relationships between Earth, the Moon, and the Sun. It explains that rotation is the turning of a body on its axis, such as Earth rotating daily, while revolution is the motion of one body around another, such as Earth revolving around the Sun yearly. It also defines insolation as the amount of solar radiation reaching Earth and describes how the tilt of Earth's axis and its revolution cause seasons by changing the Sun's angle of incidence across the globe throughout the year.