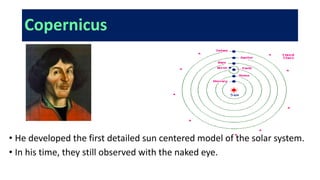
- Early models of the solar system placed Earth at the center, with planets orbiting it. Copernicus developed the first sun-centered model, though observations were still made with the naked eye. Galileo made improvements to the telescope and observed Jupiter's moons, showing Earth was not uniquely orbited.
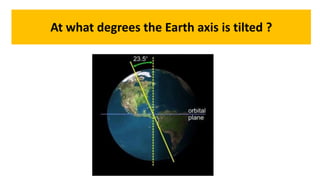
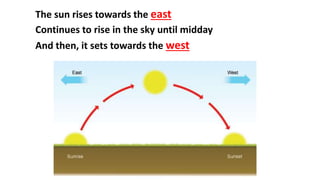
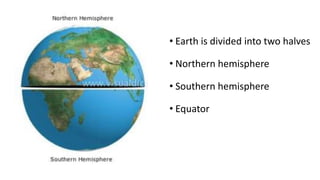
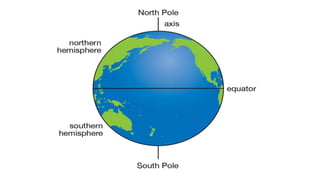
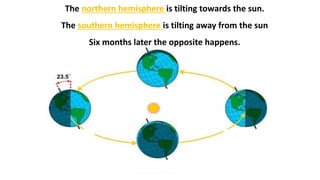
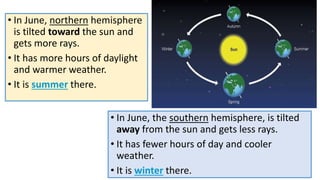
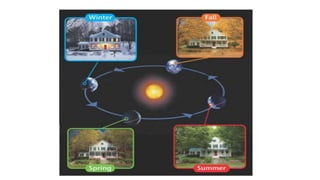
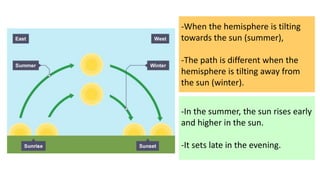
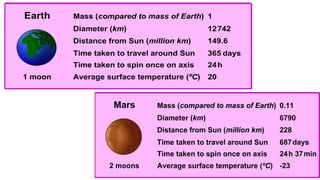
- Earth rotates on a tilted axis once every 24 hours, causing day and night as different sides face the sun. This tilt and Earth's revolution around the sun also cause the seasons in each hemisphere.
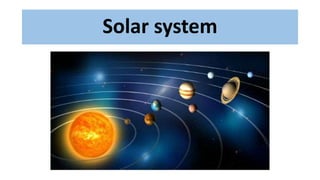
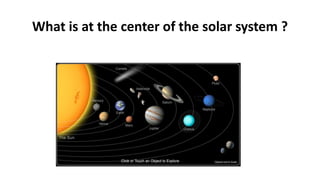
- The sun is at the center of our solar system, which includes eight planets that orbit it. Pluto is no longer classified as a planet due to its small size and irregular orbit.