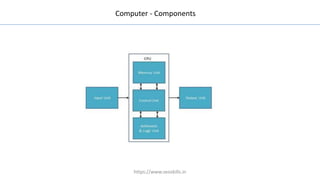
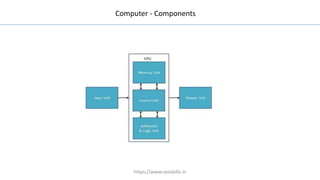
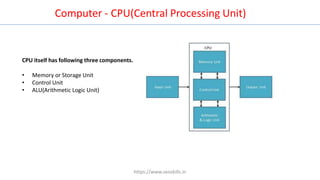
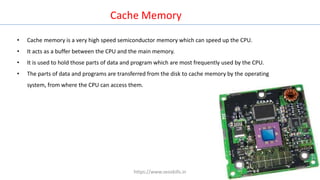
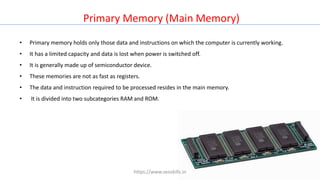
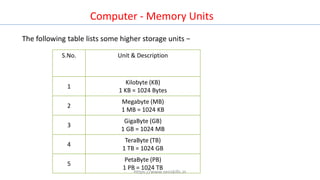
The document discusses different types of computers and their components. It describes personal computers, workstations, minicomputers, and mainframes. It then covers the main components of all computers including the central processing unit (CPU), memory (RAM, ROM), input/output devices, and motherboards. The CPU contains the control unit, arithmetic logic unit (ALU), and memory unit. RAM is further divided into static and dynamic RAM. The document provides an overview of the basic hardware that makes up all computer systems.