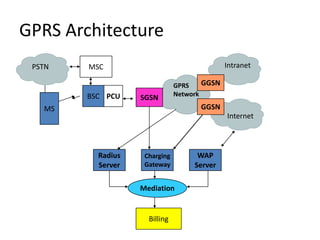
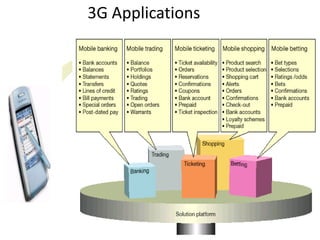
3G is a third generation wireless network technology that provides high-speed bandwidth for multimedia services combining voice and data. It can provide internet access at speeds up to 2Mbps for stationary devices and 384kbps for fast moving devices, allowing for services like email with full file attachments. The 3G network architecture includes a core network and access network connected to user equipment. It uses technologies like UMTS and WCDMA to transfer both packet-switched and circuit-switched data and provide services across different networks and service providers.