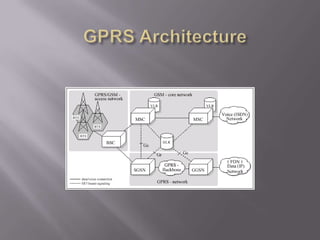
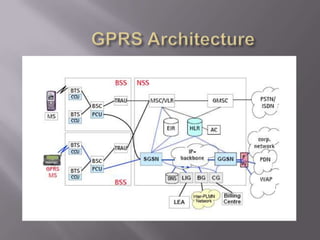
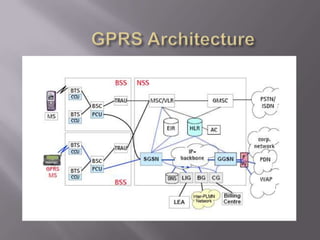
GPRS is a packet-based mobile data service on GSM networks that provides faster data transmission rates than GSM. It allows more efficient use of network resources by allowing radio channels to be shared and users to pay for the amount of data transferred rather than connection time. GPRS serves as an important step towards 3G networks by using a similar business model and network architecture. The key network elements that support GPRS include the SGSN, GGSN, PCU and DNS.