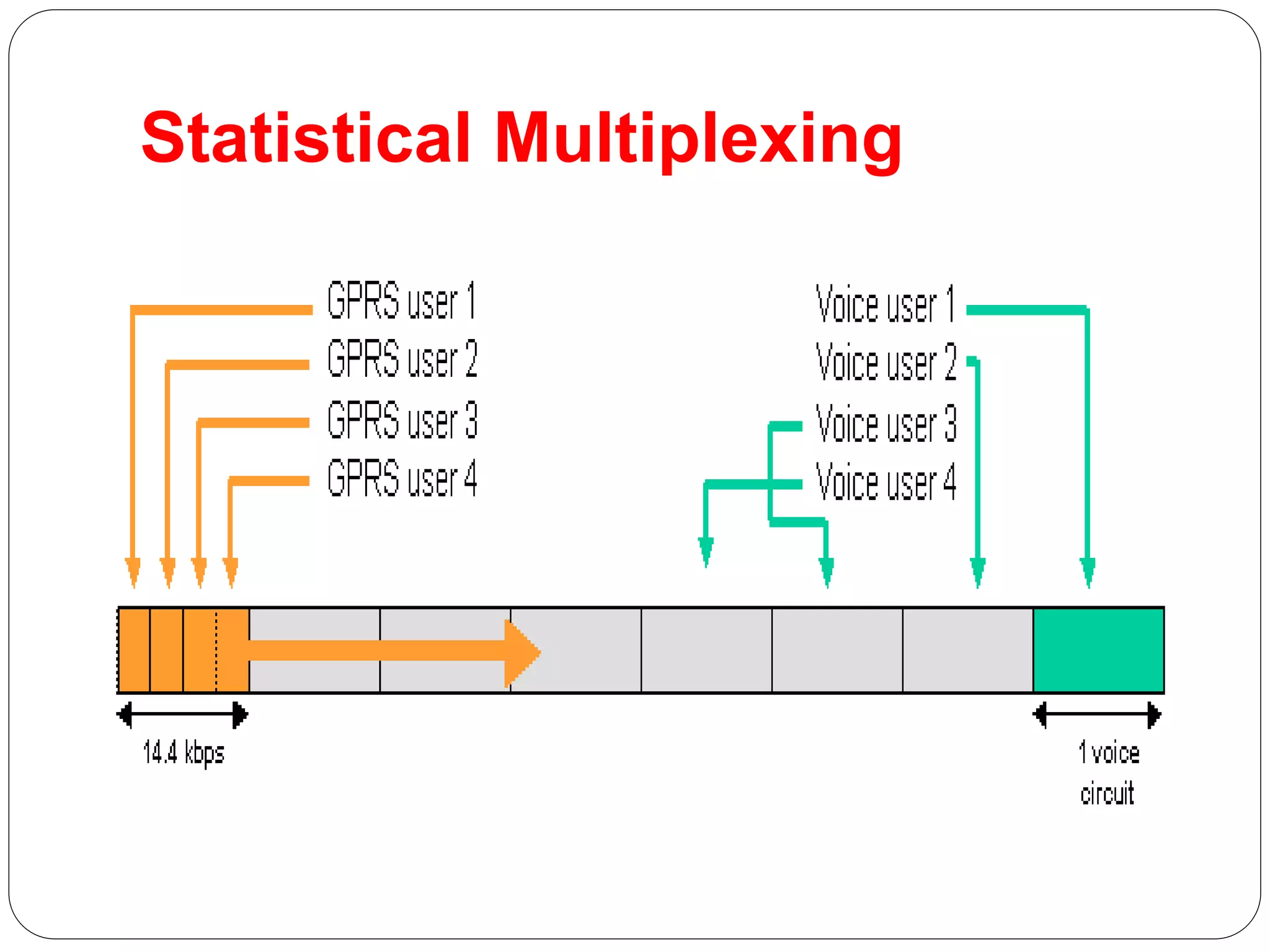
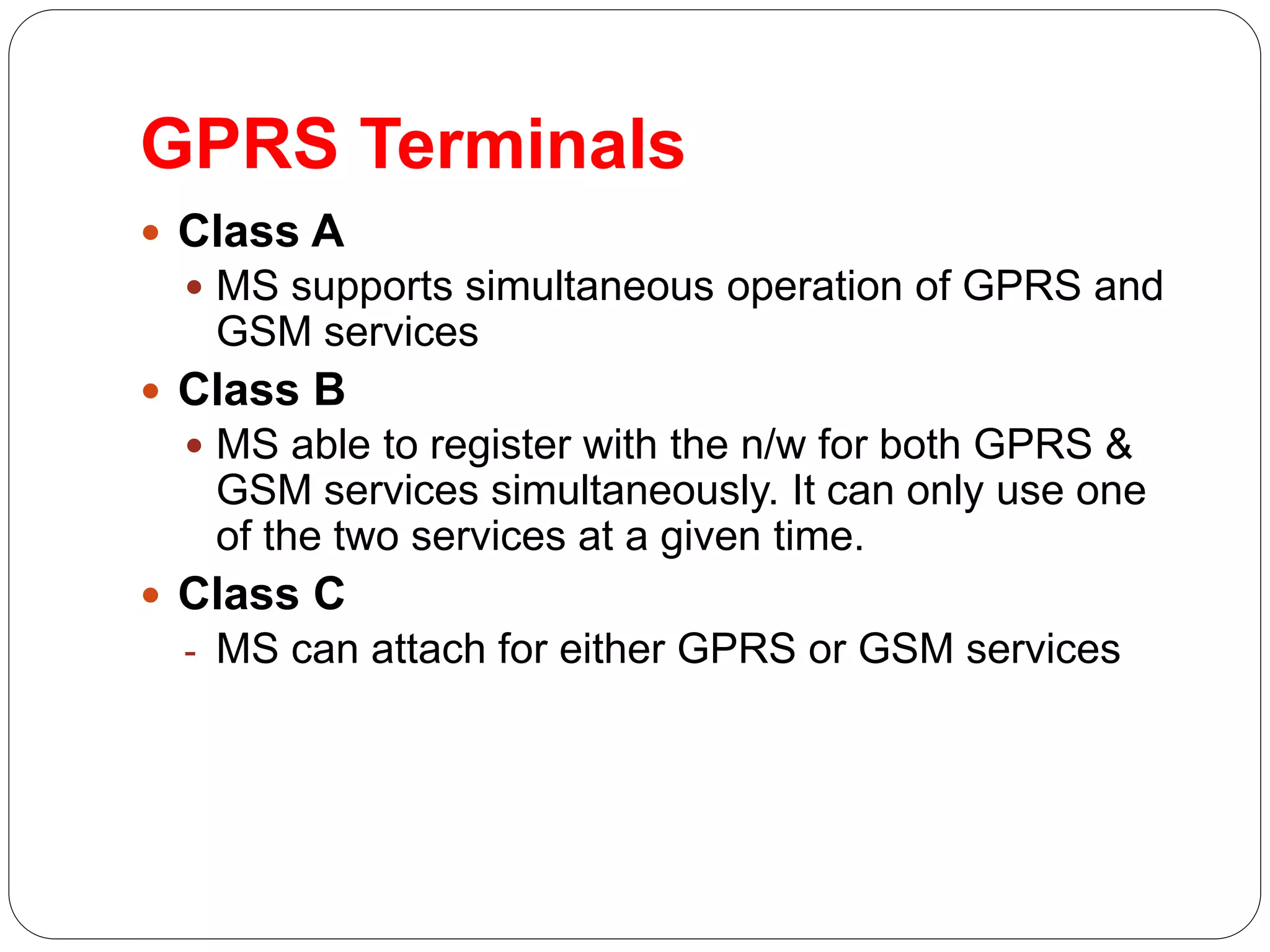
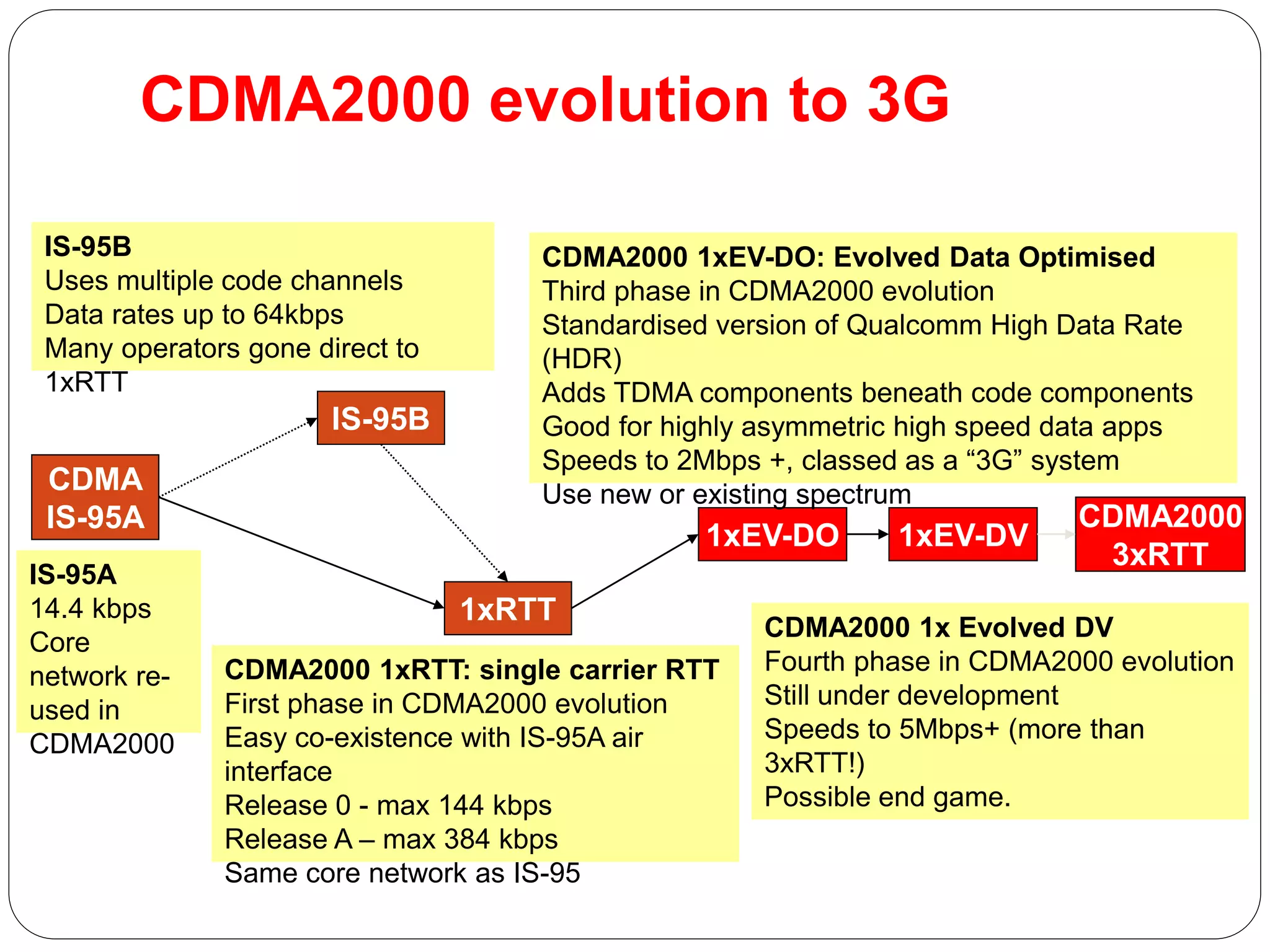
This document provides an overview of GPRS architecture and 3G cellular systems. It defines GPRS as a new bearer service for GSM that improves wireless access to packet data networks. Key benefits of GPRS include new data services, higher speeds up to 115 kbps, efficient use of bandwidth through statistical multiplexing, and constant connectivity. The document then describes statistical multiplexing and the network elements of GPRS such as SGSN, GGSN, and the GPRS register. It concludes with an overview of 3G technologies like UMTS and CDMA2000, their network architectures and frequency spectrums.