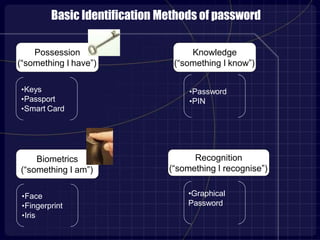
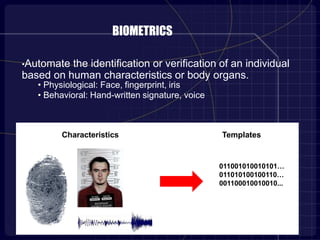
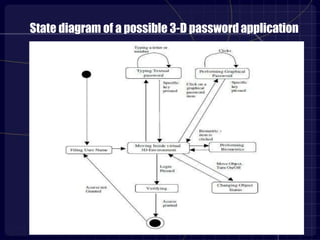
This document proposes a 3D password authentication method that combines multiple existing authentication schemes. A 3D virtual environment would contain various interactive objects like computers, fingerprint scanners, and whiteboards. A user's 3D password would consist of a sequence of actions with different objects, such as typing a text password on a computer or drawing on a whiteboard. This multi-factor approach makes 3D passwords very hard to crack compared to standard passwords. The document discusses guidelines for designing effective 3D environments and lists examples of applications and advantages, such as easy memorization and a large possible password space. However, it also notes some disadvantages like expense and difficulties for blind users.