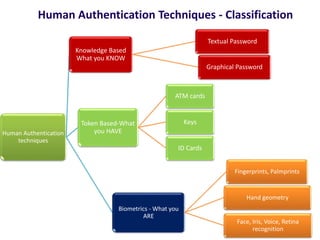
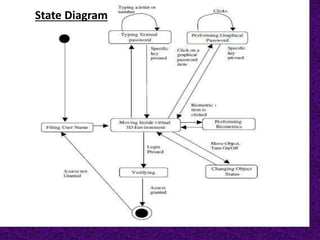
The document discusses different types of authentication techniques such as text passwords, biometric scanning, tokens, and cards. It then introduces 3D passwords as a multifactor authentication method that combines recognition, recall, tokens, and biometrics. A 3D password involves a user navigating a virtual environment and interacting with virtual objects in a certain sequence. This provides stronger security than other methods. The document outlines guidelines for designing 3D environments and discusses applications and attacks on 3D passwords. It concludes that 3D passwords could improve authentication but require further development based on user testing.