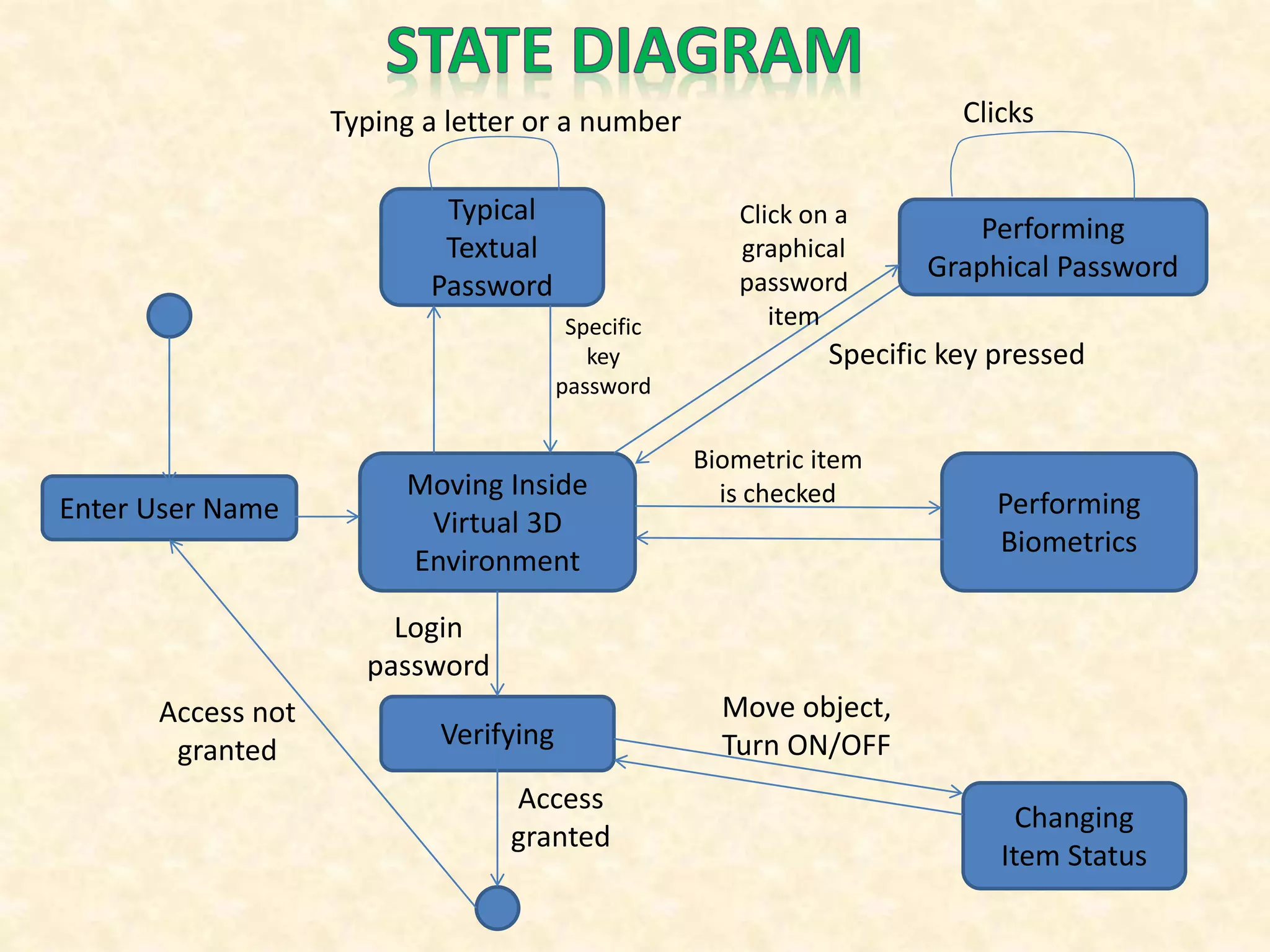
The document describes a 3D password authentication system that combines knowledge-based, token-based, and biometric authentication. The system presents a virtual 3D environment containing objects the user must interact with in a specific sequence. This provides stronger security than typical passwords by requiring the user to navigate the virtual space and interact with objects at particular locations. The 3D password scheme is difficult to crack as it has no fixed procedure and incorporates multiple authentication factors.