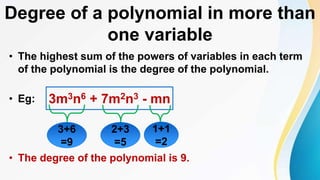
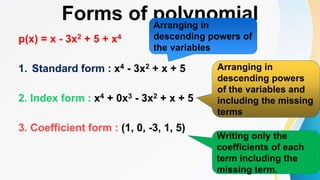
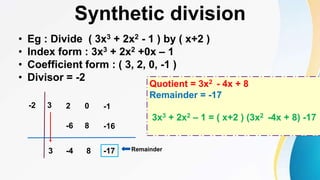
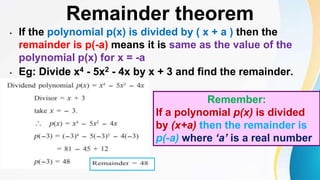
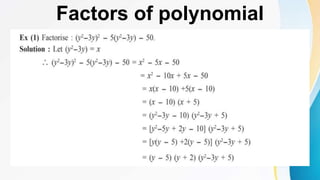
This document discusses polynomials. It defines a polynomial as an algebraic expression where the powers of the variables are whole numbers. The degree of a polynomial is the highest power of the variable. For polynomials with more than one variable, the degree is the highest sum of the powers of the variables in each term. Polynomials can be written in standard, index, or coefficient form by arranging the terms in descending powers. Polynomials can be added, subtracted, multiplied, and divided using the rules of exponents. The remainder theorem states that if a polynomial is divided by (x + a), the remainder is the value of the polynomial for x = -a.