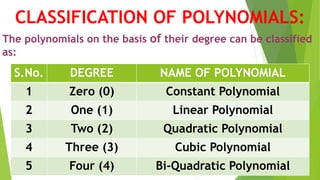
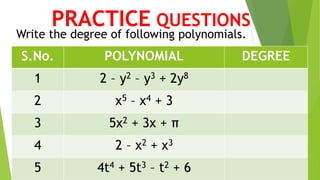
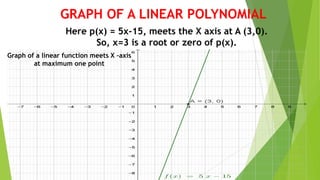
This document defines polynomials and discusses their key properties. It begins by defining a polynomial as an algebraic expression with two or more terms where the power of each variable is a positive integer. The degree of a polynomial is defined as the highest power of the variable. Polynomials are then classified based on their degree as constant, linear, quadratic, cubic, etc. The document also discusses the zeros or roots of a polynomial, which are the values that make the polynomial equal to zero. It shows how the zeros relate to the coefficients of the polynomial and can be found using factoring or solving techniques. Examples are provided to illustrate dividing polynomials using the division algorithm.