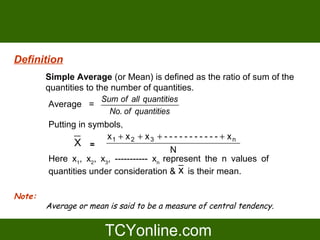
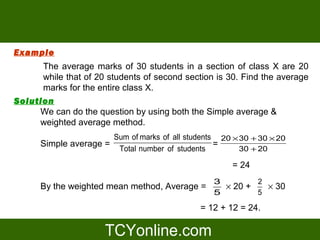
The document explains the concept of average, including simple and weighted averages, and discusses their calculations with examples. It also covers properties of averages, such as how they change with addition or multiplication of quantities. Additionally, it presents information on average speed calculation and provides related examples.