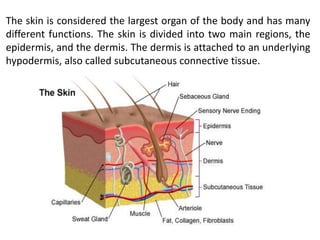
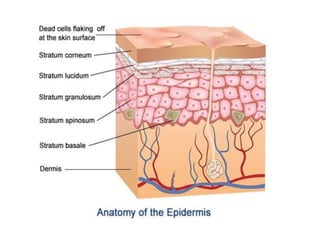
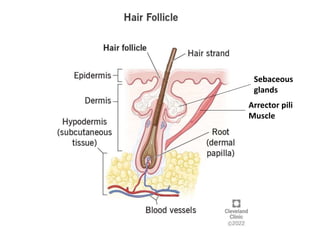
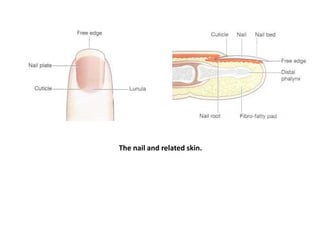
The skin is the largest organ of the body and has three main layers - the epidermis, dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis is made of stratified squamous epithelium and provides a protective barrier. It has five layers including the stratum corneum. The dermis contains collagen, elastic fibers, blood vessels, nerves and skin appendages. The hypodermis is a subcutaneous layer containing fat and lobules. Skin has several functions like protection, sensation, temperature regulation and immunity. It also contains appendages like hair, nails, sweat and sebaceous glands.