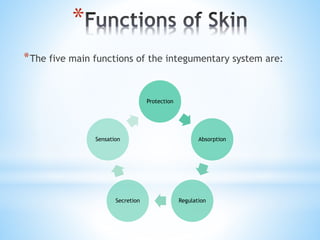
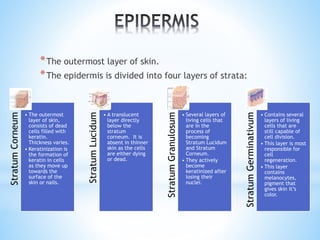
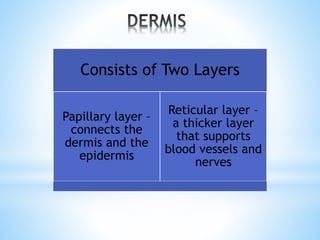
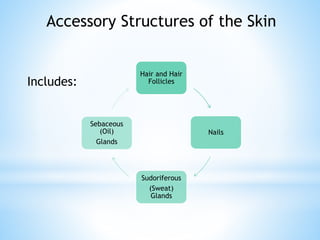
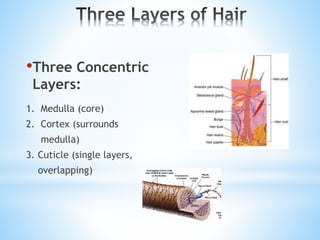
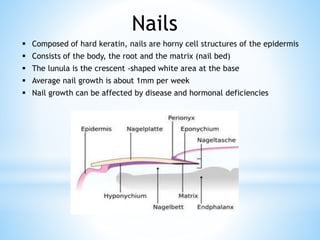
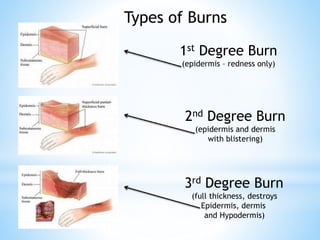
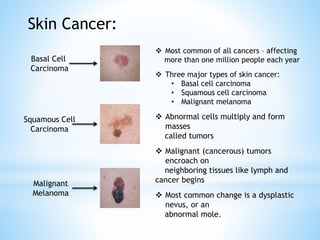
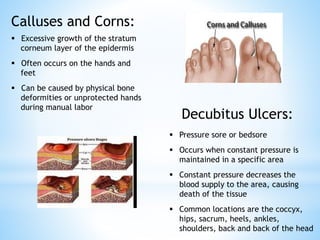
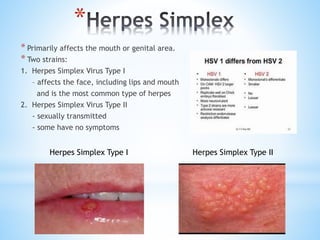
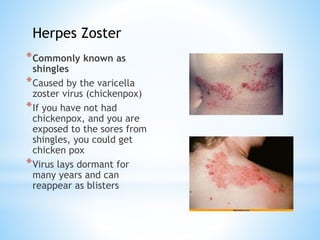
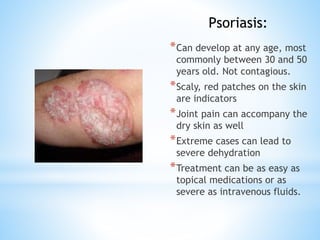
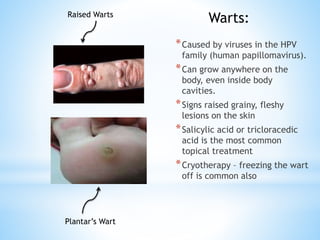
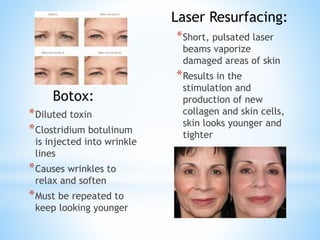
The document provides information on the integumentary system. It discusses the three layers of skin - epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous layer. It describes the five main functions of the integumentary system as protection, absorption, regulation, secretion, and sensation. Accessory structures like hair, nails, sweat and oil glands are also covered. Common disorders like burns, skin cancer, acne, and conditions like eczema, psoriasis and rosacea are summarized. Common skin treatments including microdermabrasion, chemical peels, Botox, and laser resurfacing are briefly described.