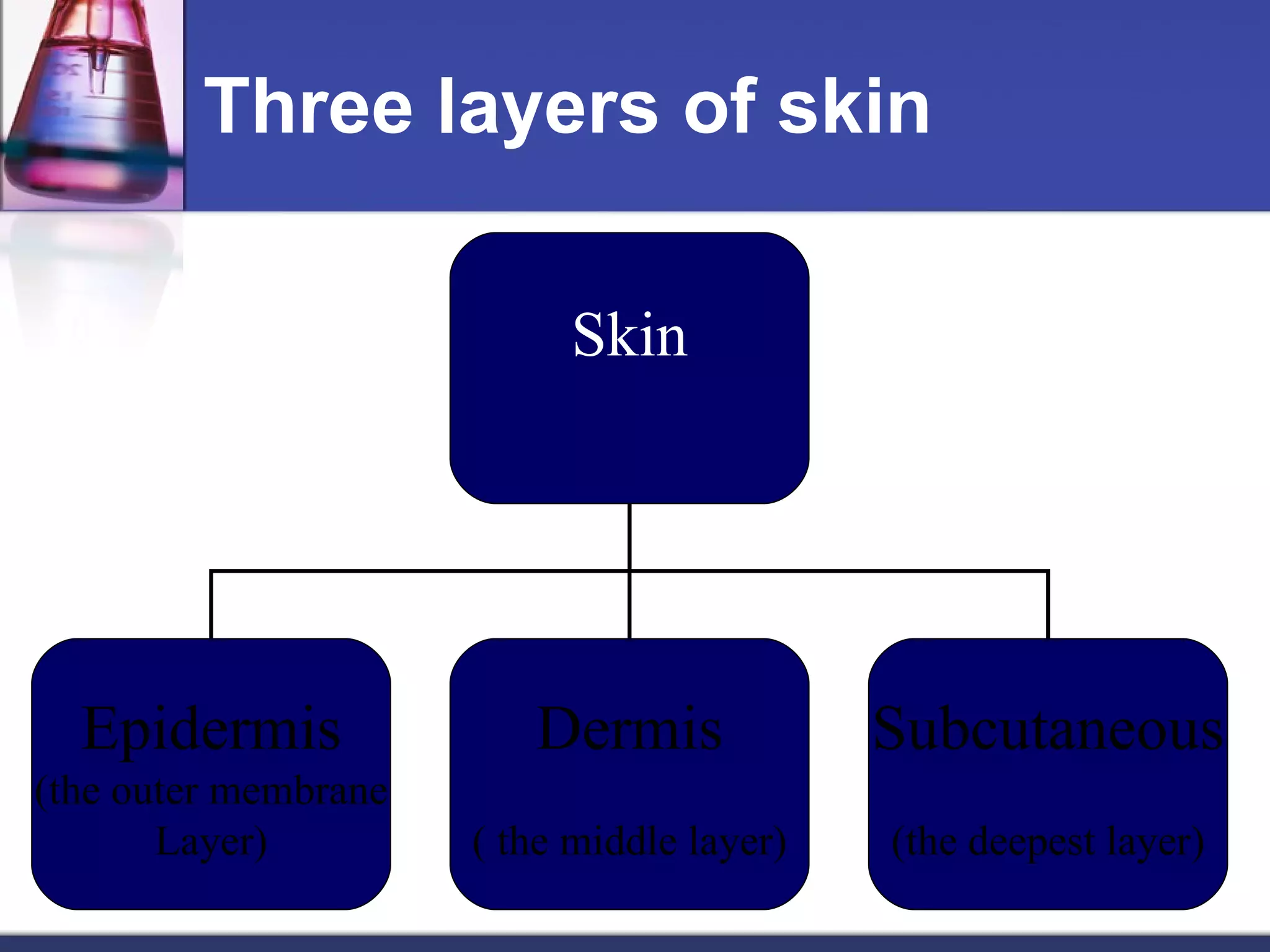
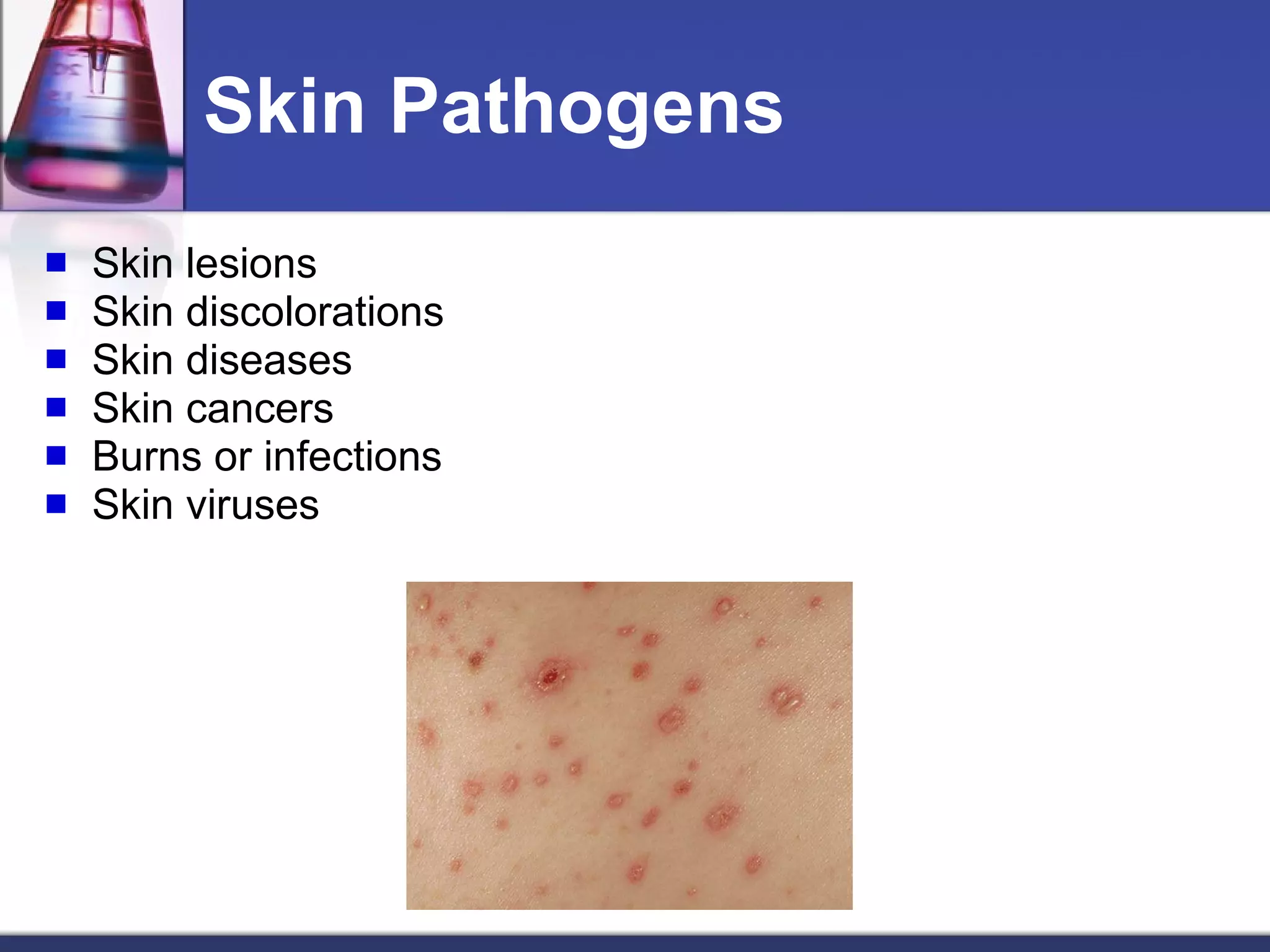
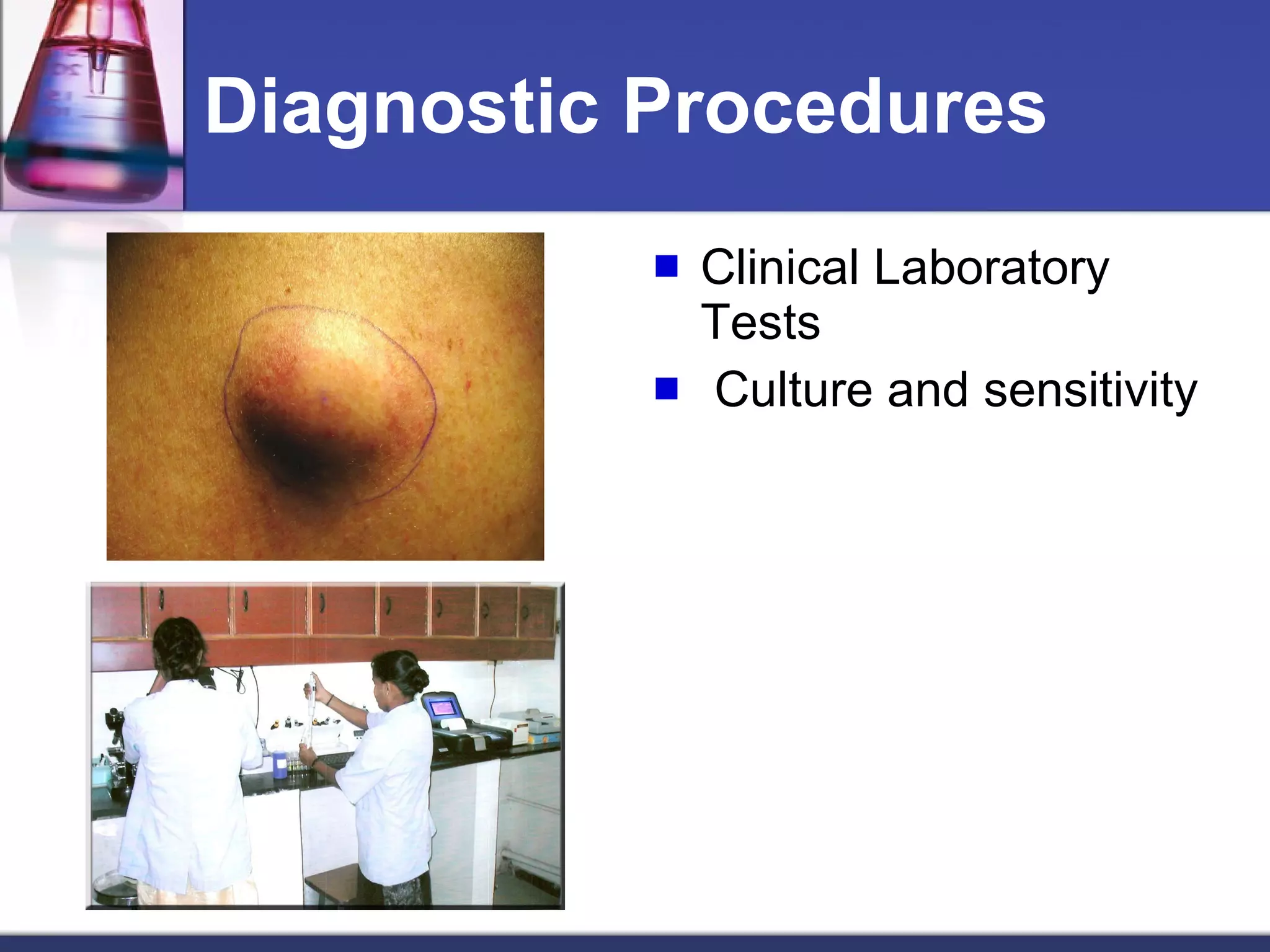
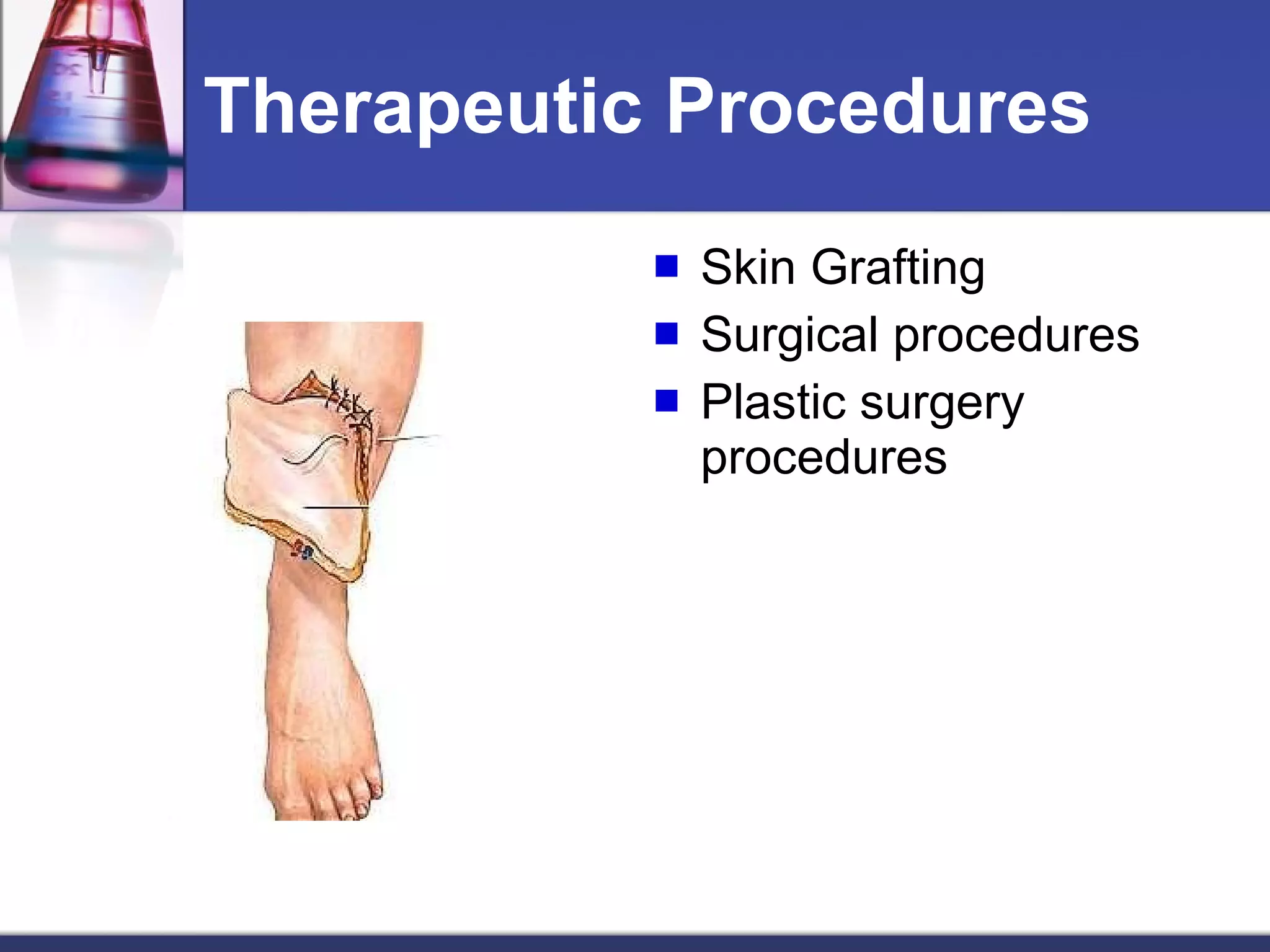
The skin is the largest organ of the body and has three main layers - the epidermis, dermis and subcutaneous layer. The epidermis is the outer layer and does not contain blood vessels, while the dermis below contains connective tissue and collagen. The deepest subcutaneous layer contains fat cells. The skin also contains sweat glands, hair follicles, nails and oil glands, and acts as a protective barrier while also sensing touch and temperature. Skin can be affected by pathogens, diseases, infections and cancers.