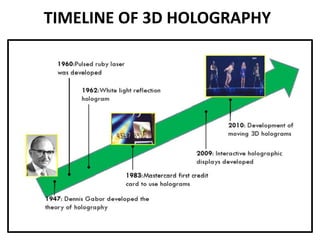
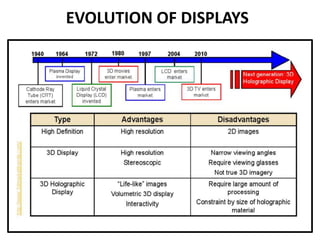
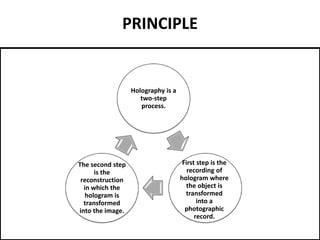
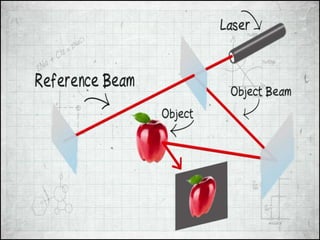
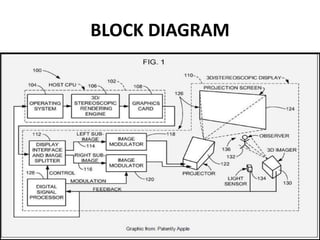
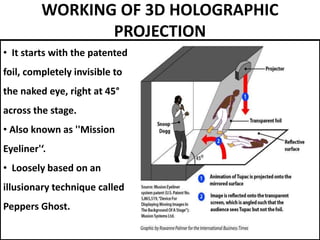
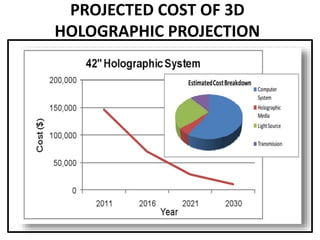
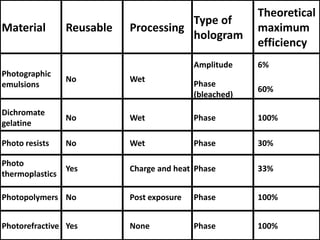
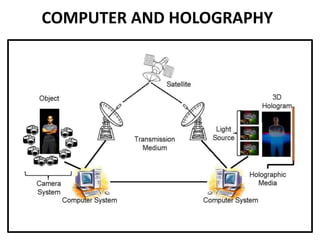
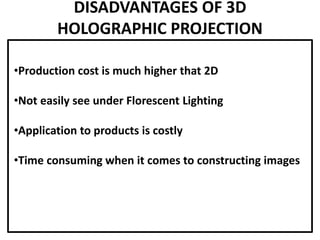
This document discusses 3D holographic projection technology. It provides an introduction to 3D holography, covering its history from Dennis Gabor's discovery in 1947 to advances enabled by lasers in the 1960s. The document outlines the working principles of 3D holographic projection using interference between light sources to create the illusion of three-dimensional imagery. Advantages include enabling glasses-free 3D viewing of virtual objects, while disadvantages include higher production costs compared to 2D. Applications discussed include entertainment, education, and medical imaging. The document concludes that holographic displays will increasingly replace other displays and enable new applications as the technology advances further.