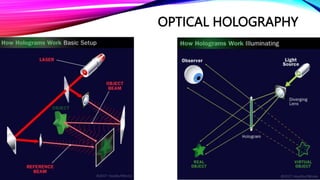
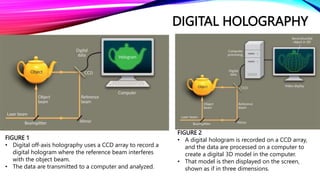
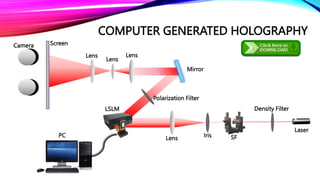
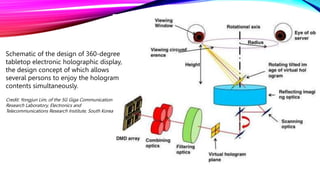
Dennis Gabor invented the hologram in 1947 and was later awarded the Nobel Prize for it. Holography records light scattered from an object to present a three-dimensional image. There are several types of holography including optical, digital, and computer generated. 3D holographic projection technology is based on Pepper's Ghost and was first used in theaters in the 1860s. Applications of 3D holographic projection include marketing, education, medical diagnostics, entertainment, conferences, home use, virtual reality, the military, and engineering.