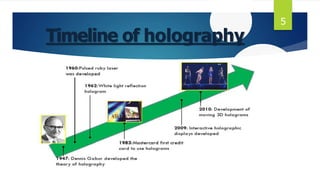
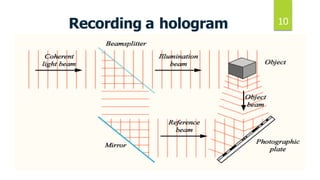
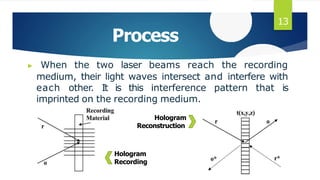
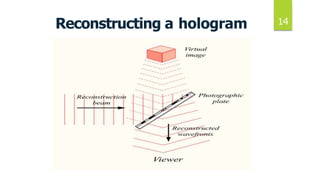
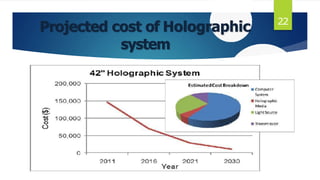
This document discusses 3D holographic projection technology. It begins by defining holography as a technique that records and reconstructs light scattered from an object to preserve its 3D information. It then covers the basic components and process for recording and reconstructing holograms, as well as advances and applications of the technology. Key points include: holograms allow for glasses-free 3D displays without a projection screen; recording involves splitting a laser beam between an object and reference beam which interfere to imprint a pattern on film; reconstruction illuminates the film to regenerate the 3D image. Future applications may include improved virtual and augmented reality, telepresence, and holographic displays replacing all screen types.