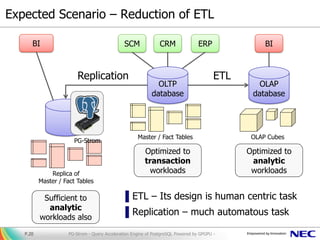
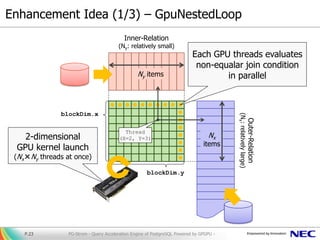
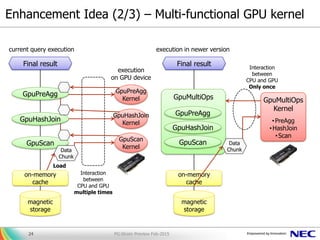
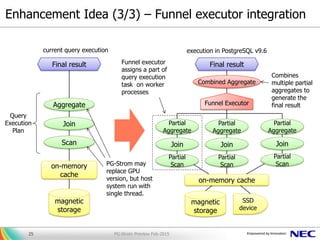
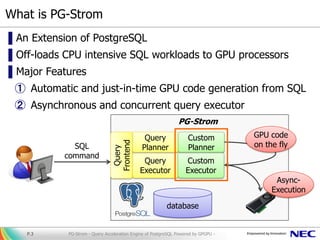
The document presents PG-Strom, an extension for PostgreSQL that accelerates query processing by leveraging GPU resources for heavy SQL computations. Key features include automatic GPU code generation, an asynchronous query executor, and compatibility with existing PostgreSQL tools, eliminating the need for extensive database tuning. Future developments aim to enhance functionality and integration with newer technologies while promoting the project's open-source nature.




![World of current cpu/memory bottleneck
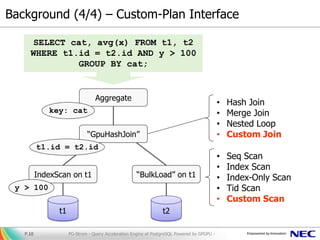
Join, Aggregation, Sort, Projection, ...
[strategy]
• burstable access pattern
• parallel algorithm
World of traditional disk-i/o bottleneck
SeqScan, IndexScan, ...
[strategy]
• reduction of i/o (size, count)
• distribution of disk (RAID)
RDBMS and bottleneck (2/2)
DB Tech Showcase 2014 Tokyo; PG-Strom - GPGPU acceleration on PostgreSQLPage. 6
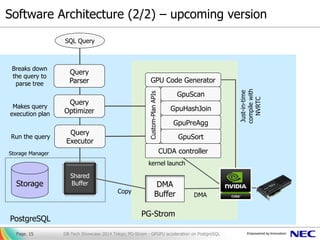
Processor
RAM
Storage
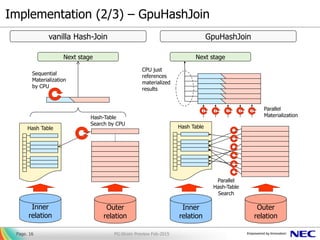
bandwidth:
multiple
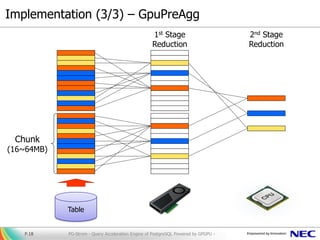
hundreds GB/s
bandwidth:
multiple GB/s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20150318-sfpug-meetup-kaigai-150319005255-conversion-gate01/85/20150318-SFPUG-Meetup-PGStrom-6-320.jpg)
![Background (3/4) – How GPU works
●item[0]
step.1 step.2 step.4step.3
Computing
the sum of array:
𝑖𝑡𝑒𝑚[𝑖]
𝑖=0…𝑁−1
with N-cores of GPU
◆
●
▲ ■ ★
● ◆
●
● ◆ ▲
●
● ◆
●
● ◆ ▲ ■
●
● ◆
●
● ◆ ▲
●
● ◆
●
item[1]
item[2]
item[3]
item[4]
item[5]
item[6]
item[7]
item[8]
item[9]
item[10]
item[11]
item[12]
item[13]
item[14]
item[15]
Total sum of items[]
with log2N steps
Inter core synchronization by HW support](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20150318-sfpug-meetup-kaigai-150319005255-conversion-gate01/85/20150318-SFPUG-Meetup-PGStrom-9-320.jpg)




![Benchmark result (1/2) – simple tables join
▌Benchmark Query:
SELECT * FROM t0 NATURAL JOIN t1 [NATURAL JOIN ....];
▌Environment:
t0 has 100million rows (13GB), t1-t9 has 40,000 rows for each, all-data pre-loaded
CPU: Xeon E5-2670v3 (12C, 2.3GHz) x2, RAM: 384GB, GPU: Tesla K20c x1
PG-Strom - Query Acceleration Engine of PostgreSQL Powered by GPGPU -P.17
18.19 19.45 21.04 23.66 26.69
37.64 43.22 49.57 56.38
64.27
87.73
109.73
132.21
155.10
179.62
207.85
233.31
263.51
0.00
50.00
100.00
150.00
200.00
250.00
300.00
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
QueryResponseTime[sec]
number of tables joined
Simple Tables Join Benchmark
PG-Strom PostgreSQL](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20150318-sfpug-meetup-kaigai-150319005255-conversion-gate01/85/20150318-SFPUG-Meetup-PGStrom-17-320.jpg)
![Benchmark result (2/2) – Star Schema Model
▌40 typical reporting queries
▌100GB of retail / start-schema data, all pre-loaded
▌Environment
CPU: Xeon E5-2670v3(12C, 2.3GHz) x2, RAM: 384GB, GPU: Tesla K20c x1
PG-Strom - Query Acceleration Engine of PostgreSQL Powered by GPGPU -P.19
0.00
200.00
400.00
600.00
800.00
1000.00
1200.00
1400.00
1600.00
1800.00
2000.00
Q.01
Q.02
Q.03
Q.04
Q.05
Q.06
Q.07
Q.08
Q.09
Q.10
Q.11
Q.12
Q.13
Q.14
Q.15
Q.16
Q.17
Q.18
Q.19
Q.20
Q.21
Q.22
Q.23
Q.24
Q.25
Q.26
Q.27
Q.28
Q.29
Q.30
Q.31
Q.32
Q.33
Q.34
Q.35
Q.36
Q.37
Q.38
Q.39
Q.40
QueryResponseTime[sec]
Typical Reporting Queries on Retail / Star-Schema Data
PG-Strom PostgreSQL](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20150318-sfpug-meetup-kaigai-150319005255-conversion-gate01/85/20150318-SFPUG-Meetup-PGStrom-19-320.jpg)