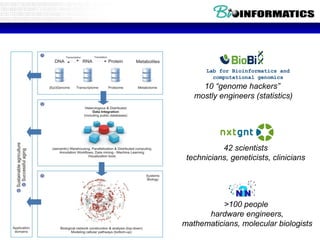
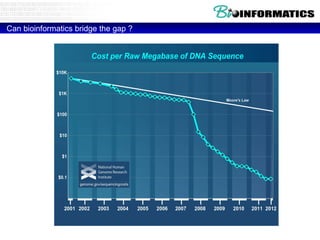
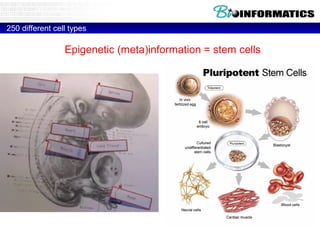
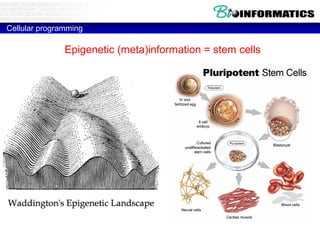
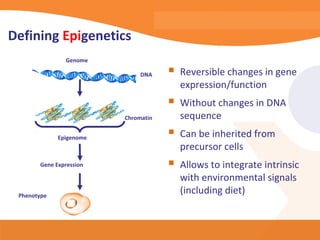
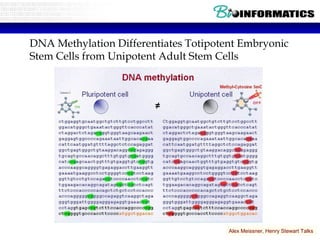
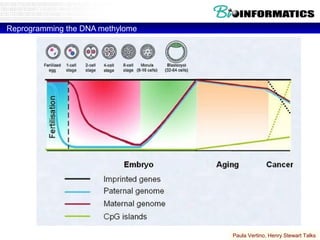
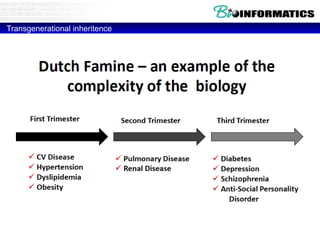
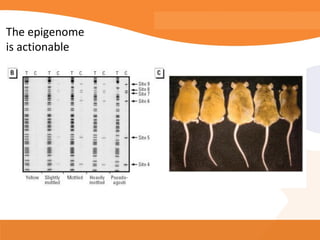
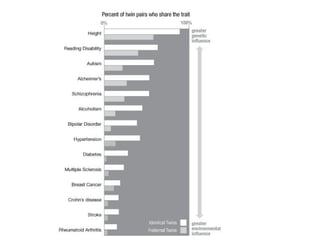
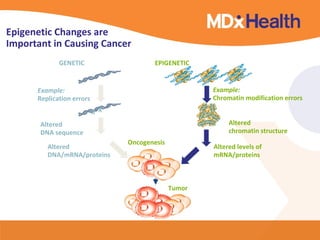
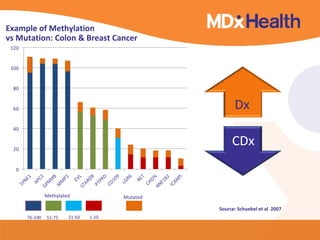
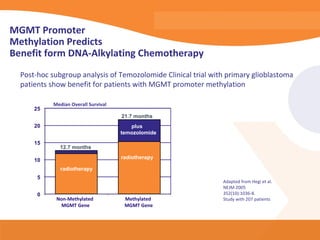
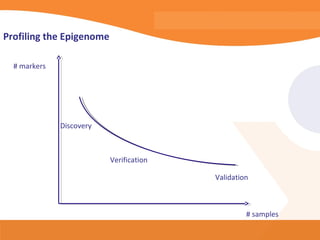
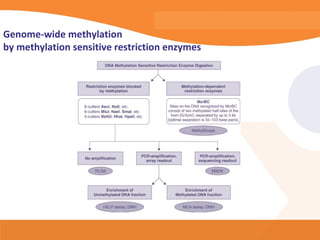
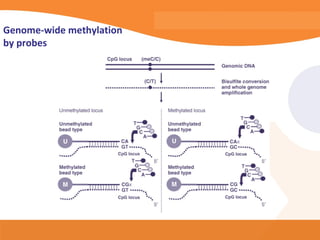
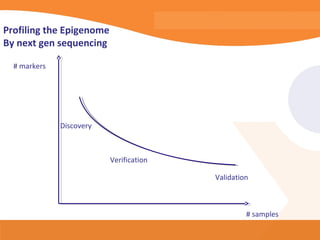
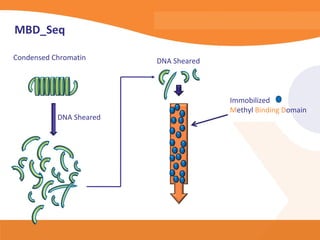
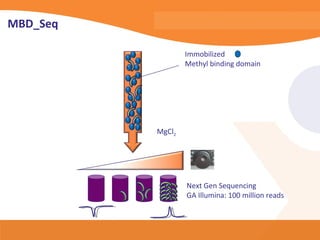
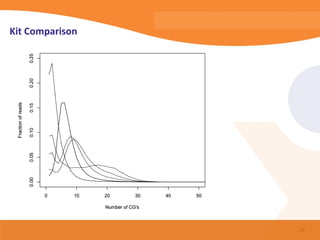
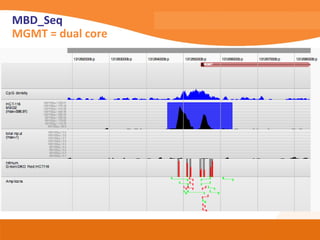
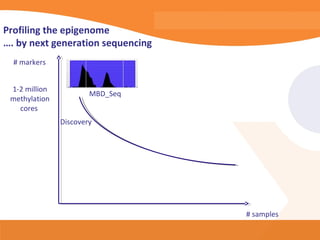
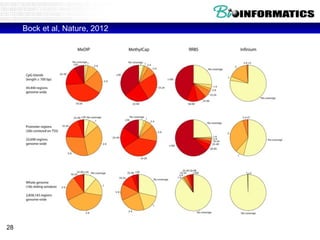
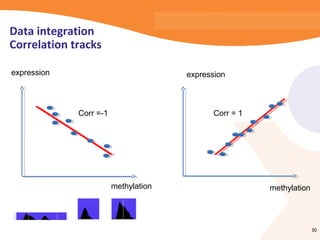
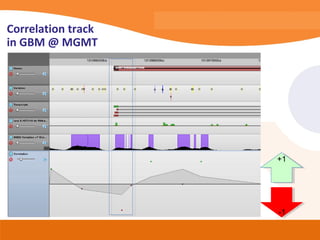
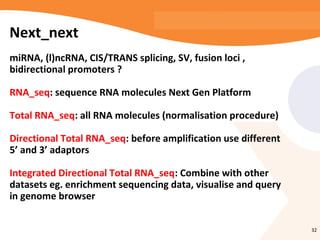
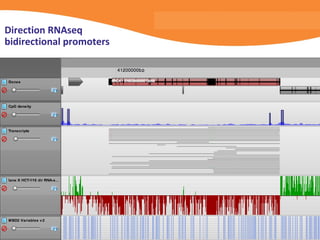
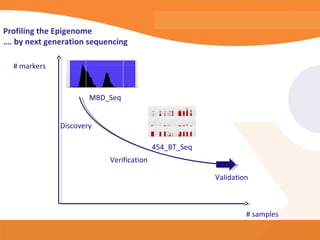
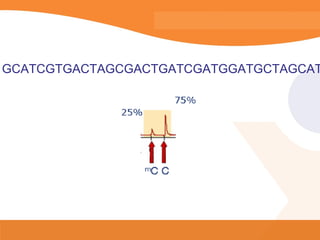
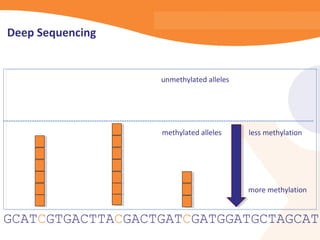
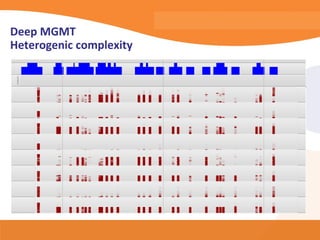
This document discusses bioinformatics and the epigenome. It notes that the lab has over 100 people from diverse backgrounds including engineers, geneticists, and molecular biologists. It then discusses how epigenetic information like DNA methylation allows for cellular programming and differentiation of stem cells. The rest of the document discusses techniques for profiling the epigenome like MBD-Seq and integration of epigenomic data with other omics datasets to better understand gene regulation and phenotypes. It emphasizes that combining multiple sequencing techniques provides the best approach and that bioinformatics challenges include normalization and data visualization.