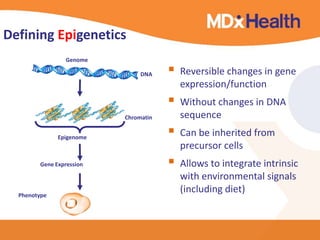
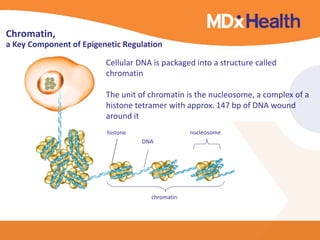
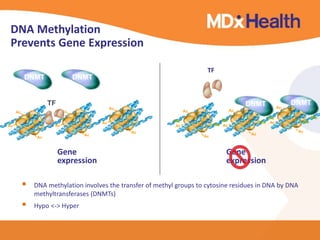
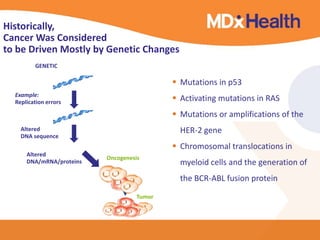
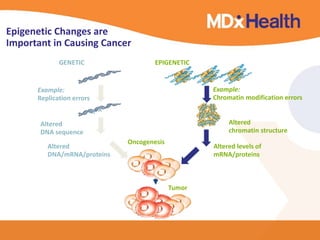
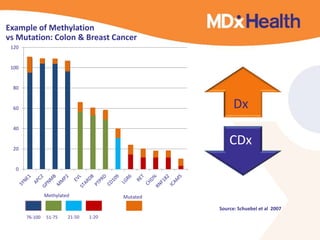
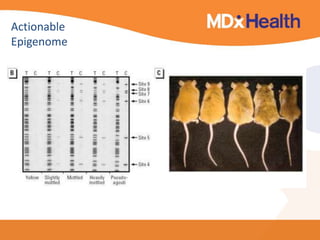
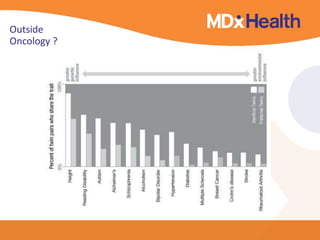
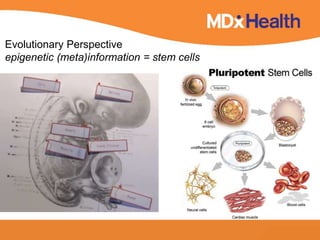
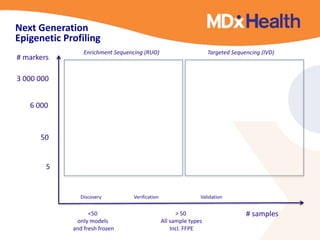
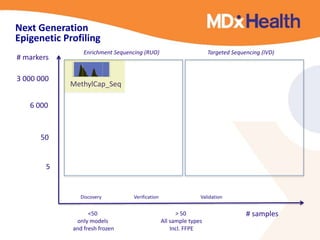
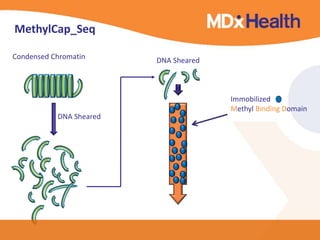
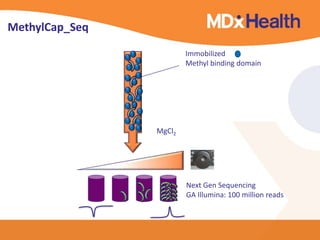
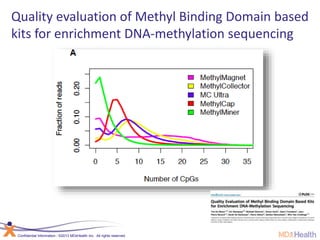
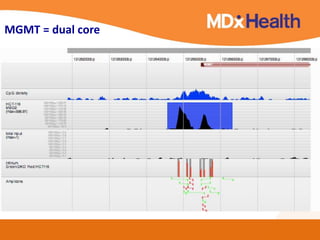
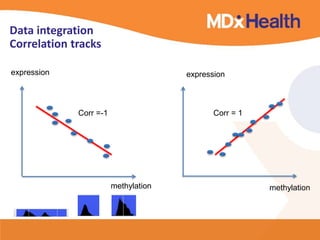
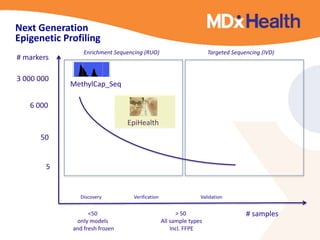
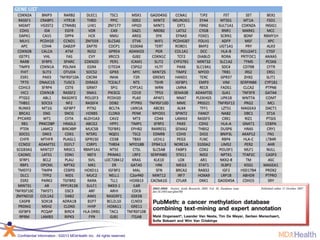
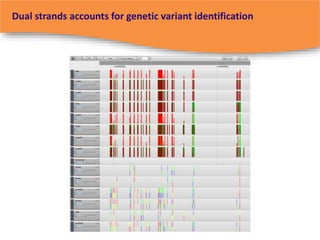
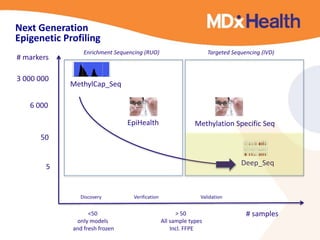
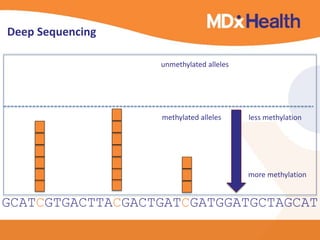
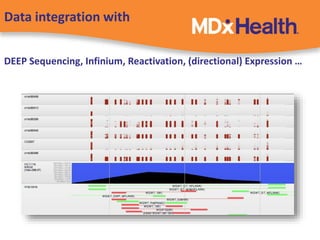
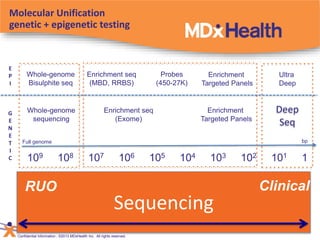
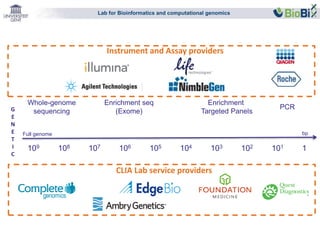
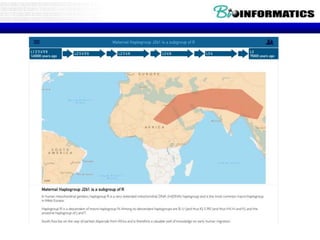
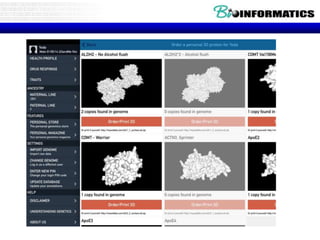
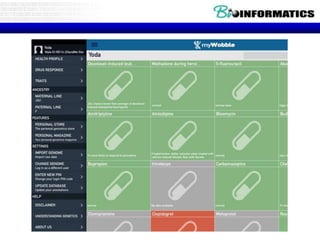
The document summarizes a presentation on bioinformatics case studies focusing on epigenetics and personal genomics. It discusses DNA methylation and its role in cancer development. It also describes how next-generation sequencing can be used to identify epigenetic biomarkers for clinical use. Finally, it addresses issues around personal and recreational genomics, including increasing access, educating users, and protecting individual privacy and rights.