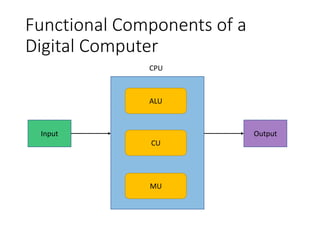
This document provides an overview of the functional components of a computing system, including the input, central processing, memory, and output units. The central processing unit (CPU) is made up of three main components: the arithmetic logic unit (ALU) which performs calculations and logical operations, the control unit which controls data flow and operations, and memory registers for temporary storage. The memory unit stores data and instructions using technologies like static RAM and dynamic RAM. Together these components allow a computer to process input according to stored instructions and provide output.