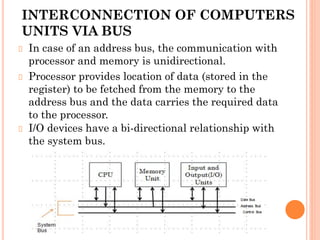
1. The document discusses the architecture and organization of computers. It describes the four main functional blocks of a computer as the central processing unit (CPU), memory, input unit, and output unit.
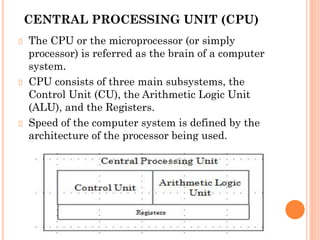
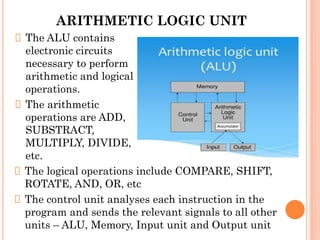
2. The CPU, which is referred to as the "brain" of the computer, consists of three main subsystems: the control unit, arithmetic logic unit (ALU), and registers. The ALU performs arithmetic and logical operations.
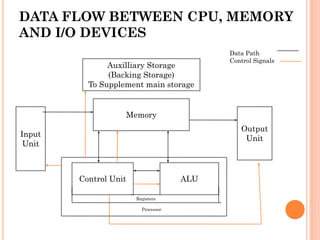
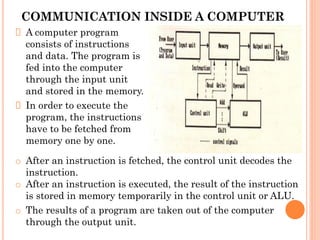
3. A computer program consists of instructions and data that are fed into memory through the input unit. The CPU fetches instructions from memory one by one and executes them, storing results temporarily in the control unit or ALU. Results are then output through the output unit.