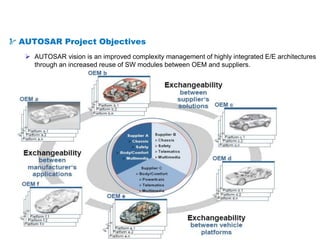
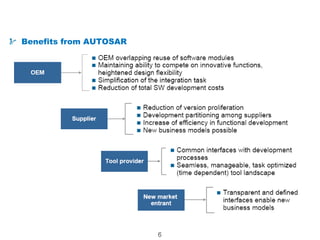
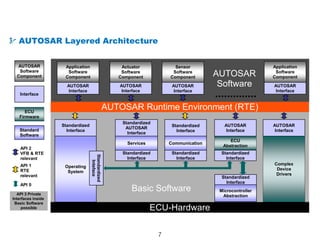
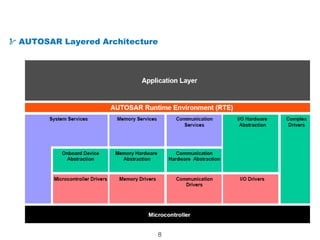
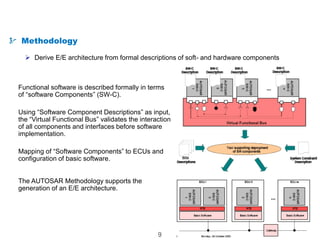
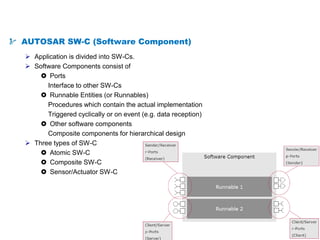
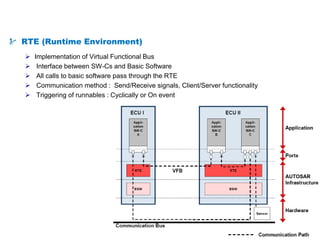
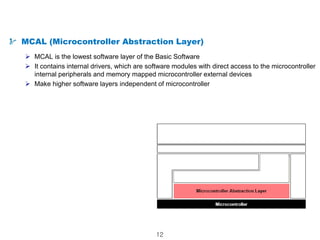
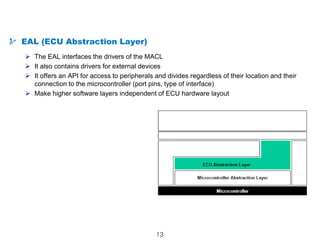
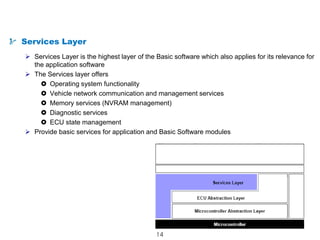
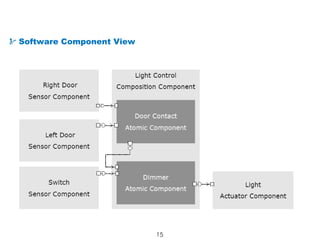
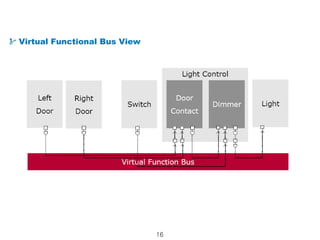
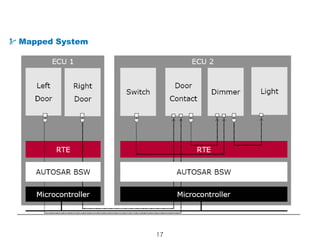
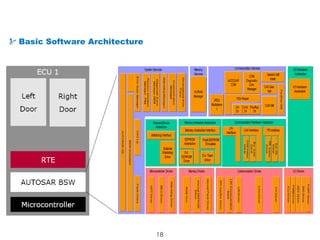
The document details the Automotive Open System Architecture (AUTOSAR), a collaborative standard aimed at managing the growing complexity of automotive embedded systems by enhancing software modularity and interface standardization. It outlines the architecture of AUTOSAR, including layered software structures and component interactions, which facilitate the development and reuse of electronic control unit (ECU) software. The ultimate goals are improved software quality, easier integration of components, and better collaboration between original equipment manufacturers and suppliers.