1) The document discusses the emergence of modern states in 15th-16th century Europe through the rise of strong monarchies like France, England, Spain, and Russia.
2) It focuses on Spain, describing the union between Castile and Aragon under the Catholic Monarchs Ferdinand and Isabella, and their efforts to centralize power and expand territories through conquest and marriage alliances.
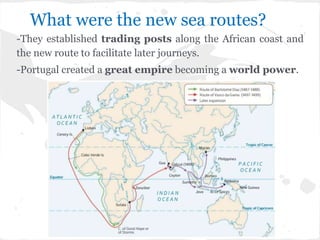
3) The Age of Discovery led Portugal to find a sea route to India by exploring along the west coast of Africa, with later Spanish expeditions reaching the Americas while seeking a route to Asia under Columbus.