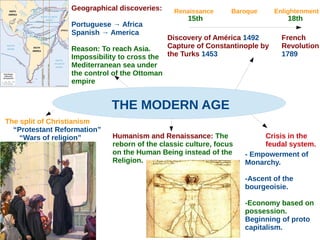
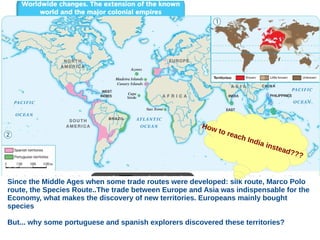
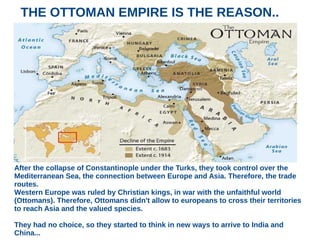
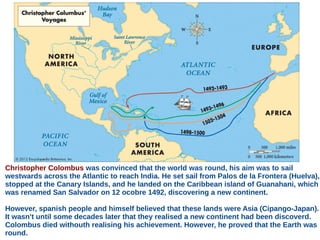
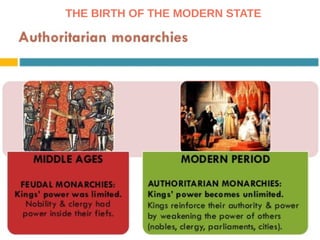
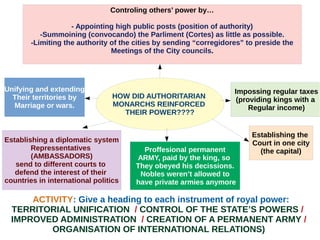
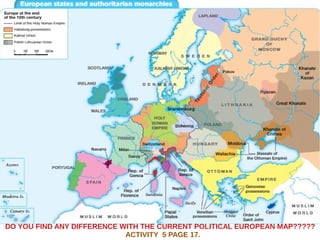
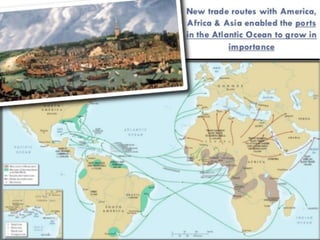
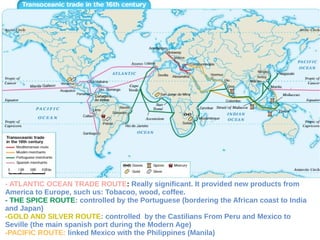
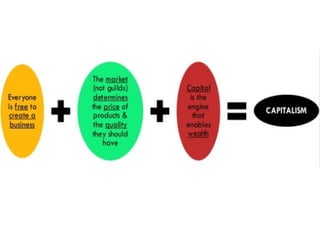
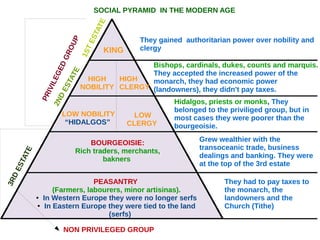
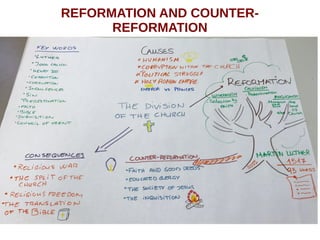
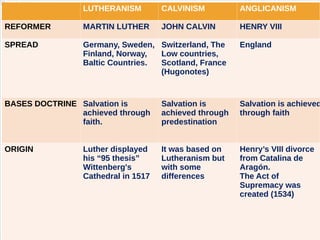
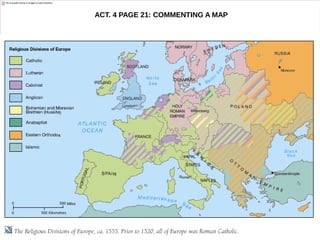
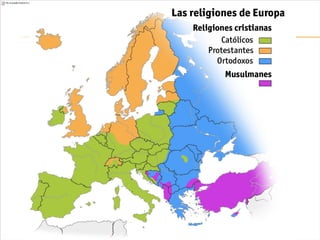
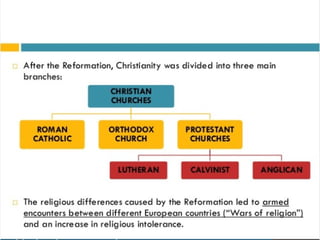
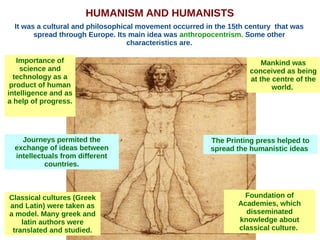
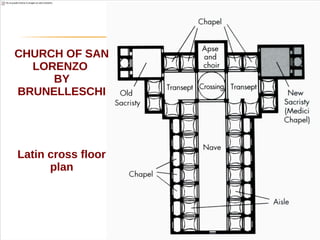
The document discusses the Middle Ages and the transition to the Modern Age across Europe from the 15th to 18th centuries. It covers several key events and developments, including the Protestant Reformation led by figures like Martin Luther and John Calvin; the Age of Discovery including Columbus' voyage to the Americas in 1492; the rise of strong monarchies and nation-states; and economic and social changes associated with the decline of feudalism and growth of trade and capitalism. The Ottoman Empire's control of the Mediterranean is cited as a factor driving European exploration of new trade routes.