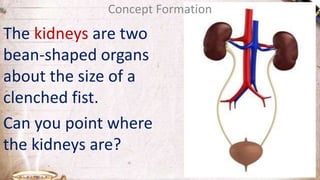
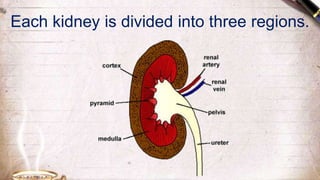
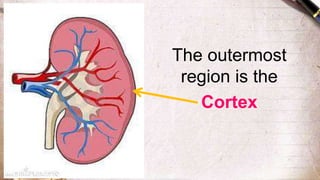
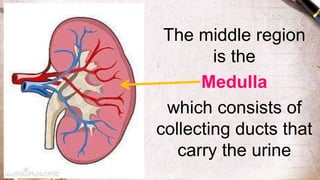
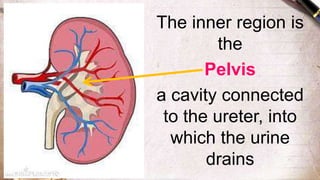
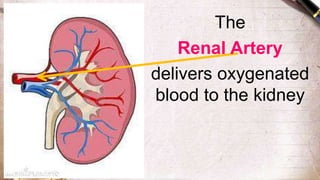
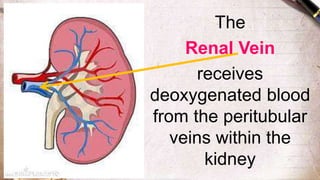
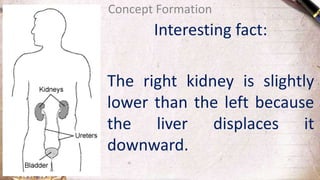
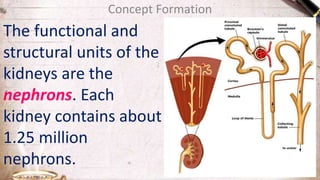
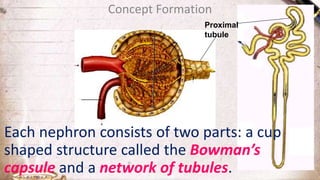
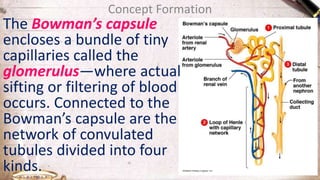
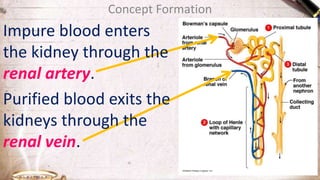
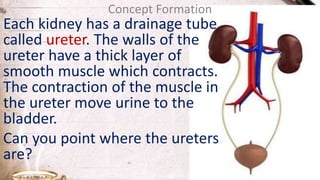
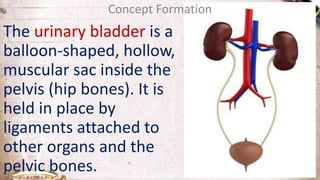
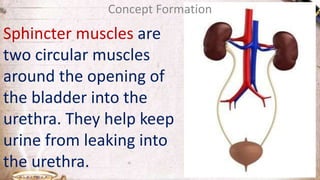
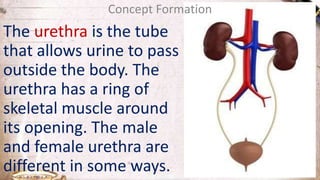
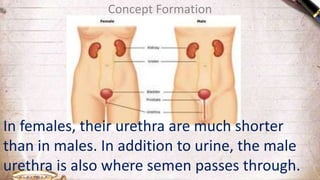
The document discusses the structure and function of the urinary system. It describes the location and roles of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. The kidneys filter waste from the blood to produce urine, and contain nephrons that remove waste and regulate chemical balances before urine passes through the ureters to the bladder for storage and eventual expulsion through the urethra.