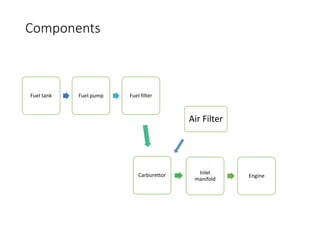
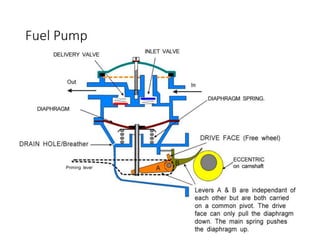
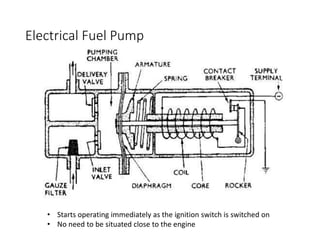
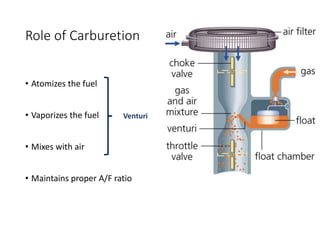
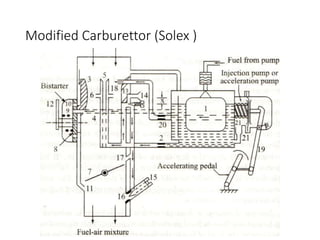
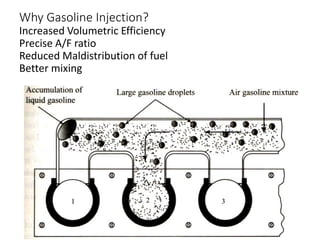
The document discusses different fuel feed systems for petrol engines, including gravity, pressure, vacuum, and pump systems. It describes key components like the fuel tank, fuel pump, fuel filter, carburetor, and inlet manifold. Carburetion is the process that atomizes, vaporizes, and mixes fuel with air to maintain the proper air-fuel ratio for combustion. Precise fuel injection systems provide benefits like increased efficiency and power compared to carbureted systems.