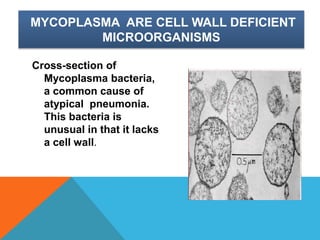
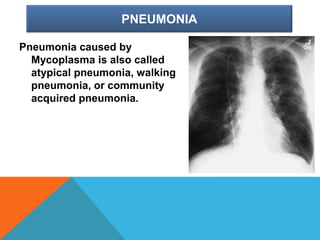
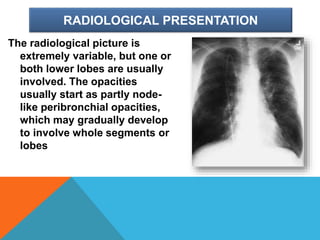
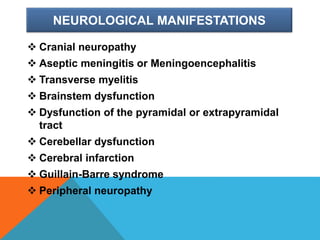
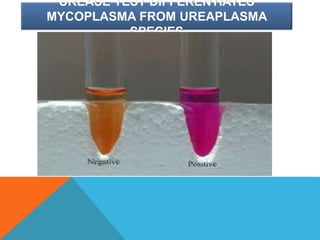
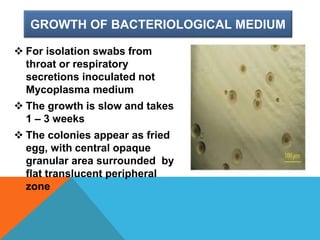
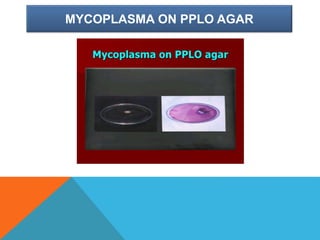
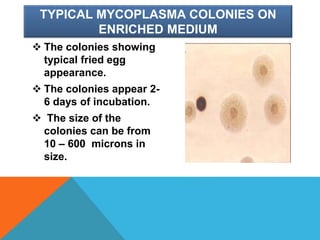
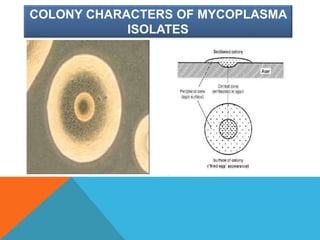
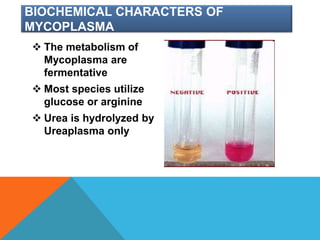
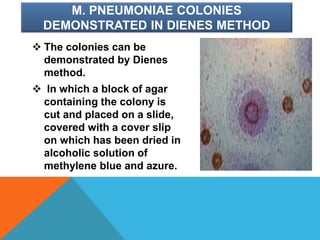
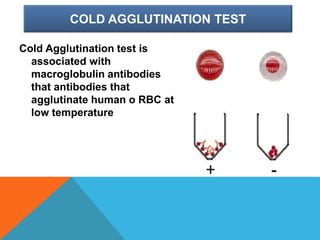
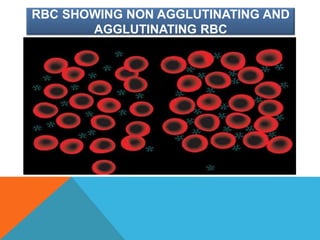
Mycoplasma are the smallest free-living organisms that lack a cell wall. They can cause respiratory infections like pneumonia (accounting for 10-20% of all pneumonias) as well as urogenital infections. Important species that infect humans include M. pneumoniae, Ureaplasma urealyticum, M. hominis, and M. genitalium. While some Mycoplasma species can be part of the normal flora, they can also cause diseases like atypical pneumonia and pelvic inflammatory disease. They are treated with antibiotics like tetracyclines but show resistance to beta-lactams due to their lack of a cell wall.