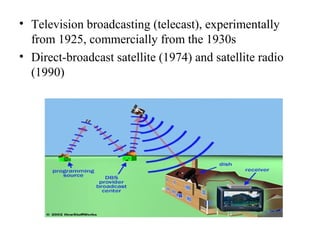
This document defines broadcasting and discusses its history and methods. It explains that broadcasting is the distribution of audio and video content to a dispersed audience using mass communication mediums like radio waves. Broadcasting began experimentally in the early 1900s and expanded with radio in the 1920s and television after World War II using new technologies. The document also outlines several economic models for broadcasting like commercial, public, and community models and distinguishes between recorded and live broadcasts.