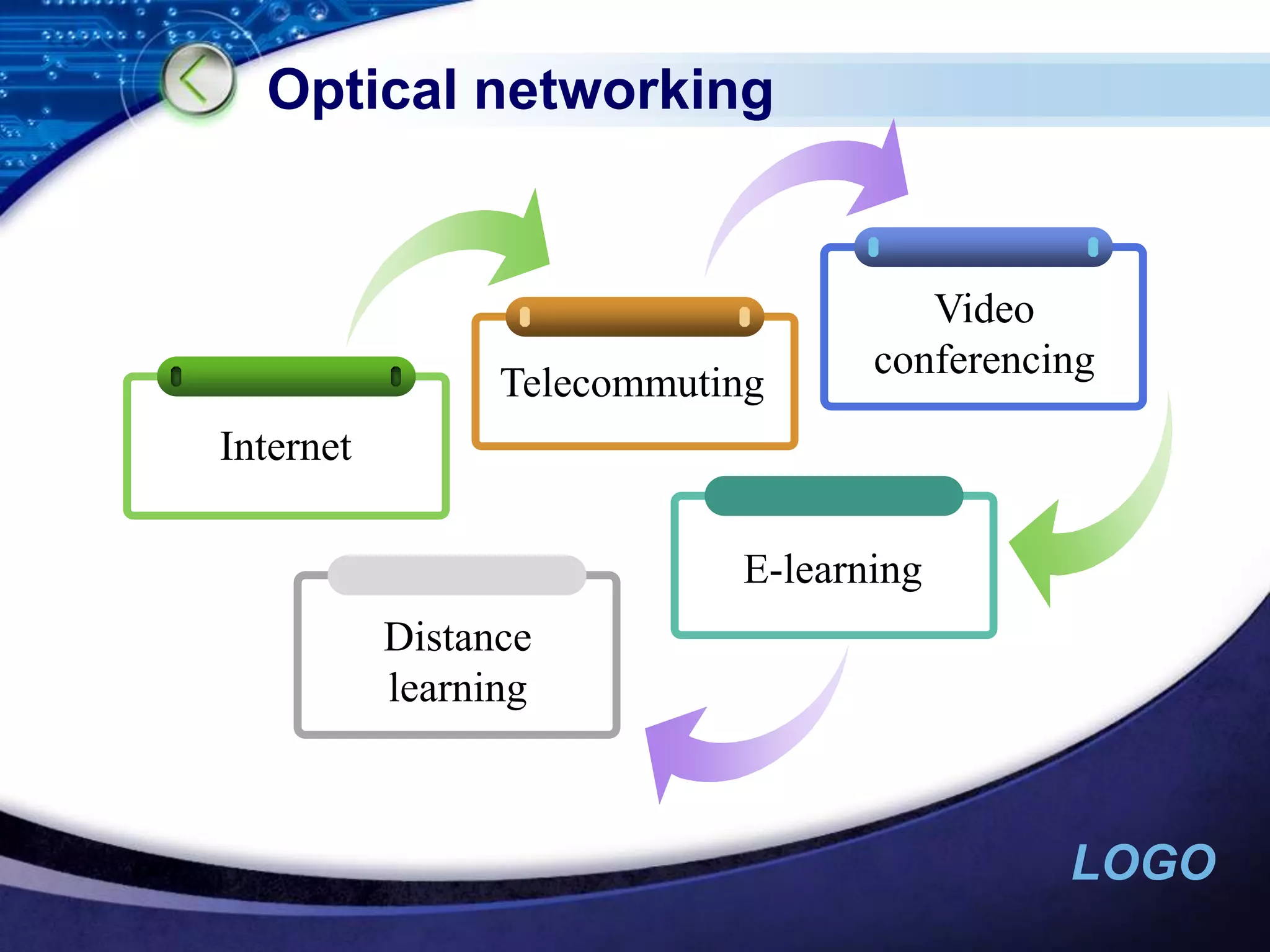
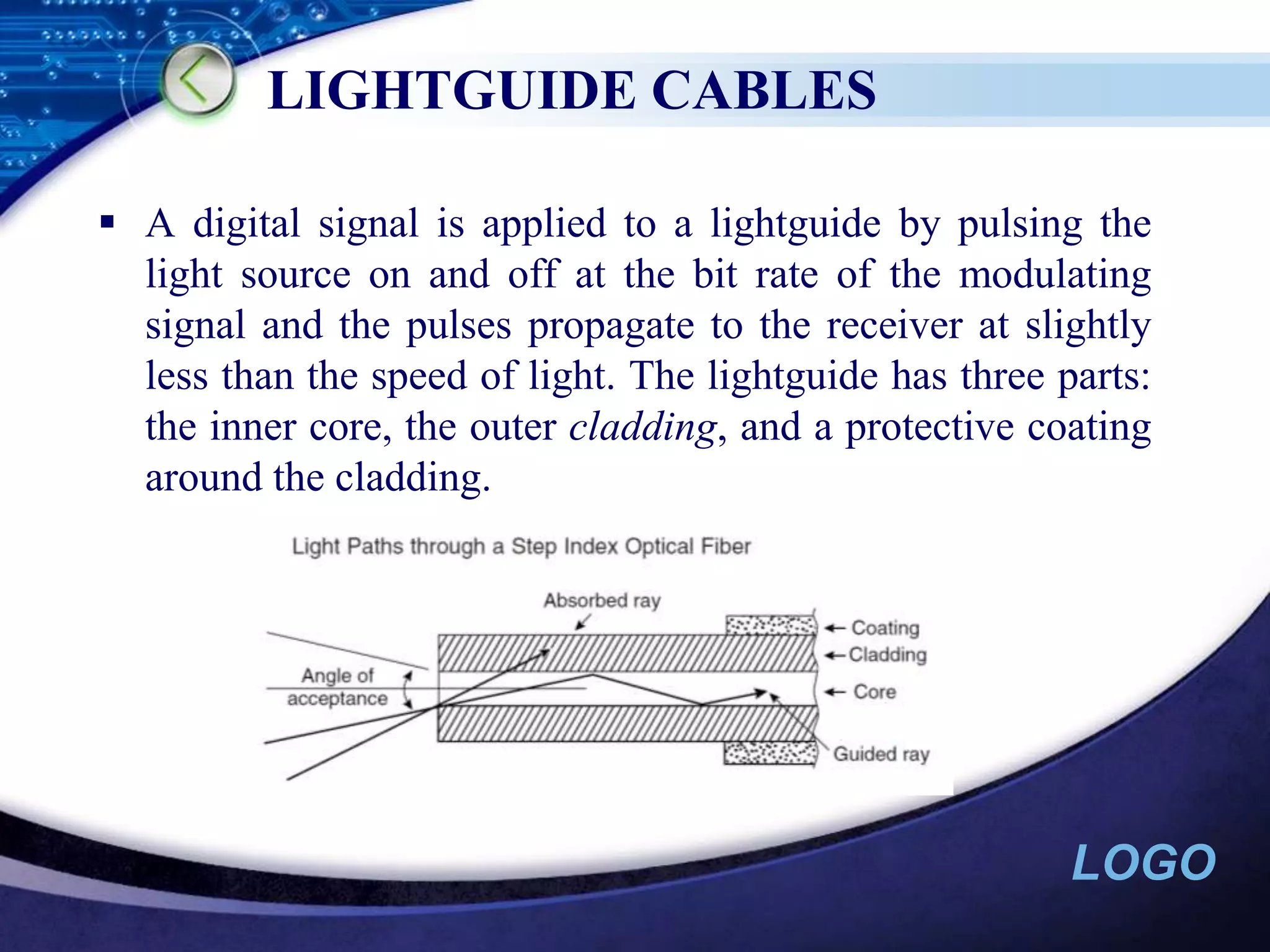
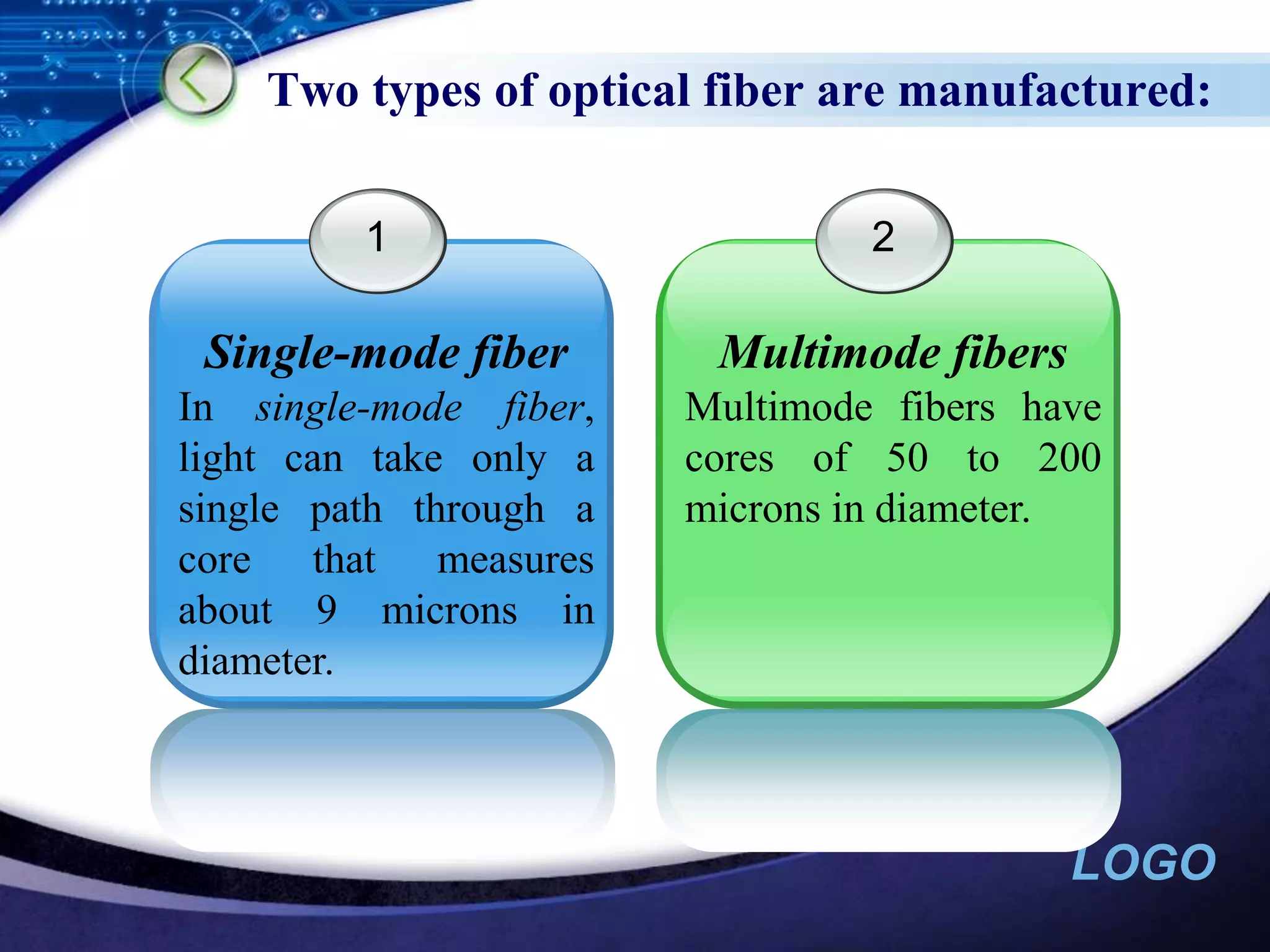
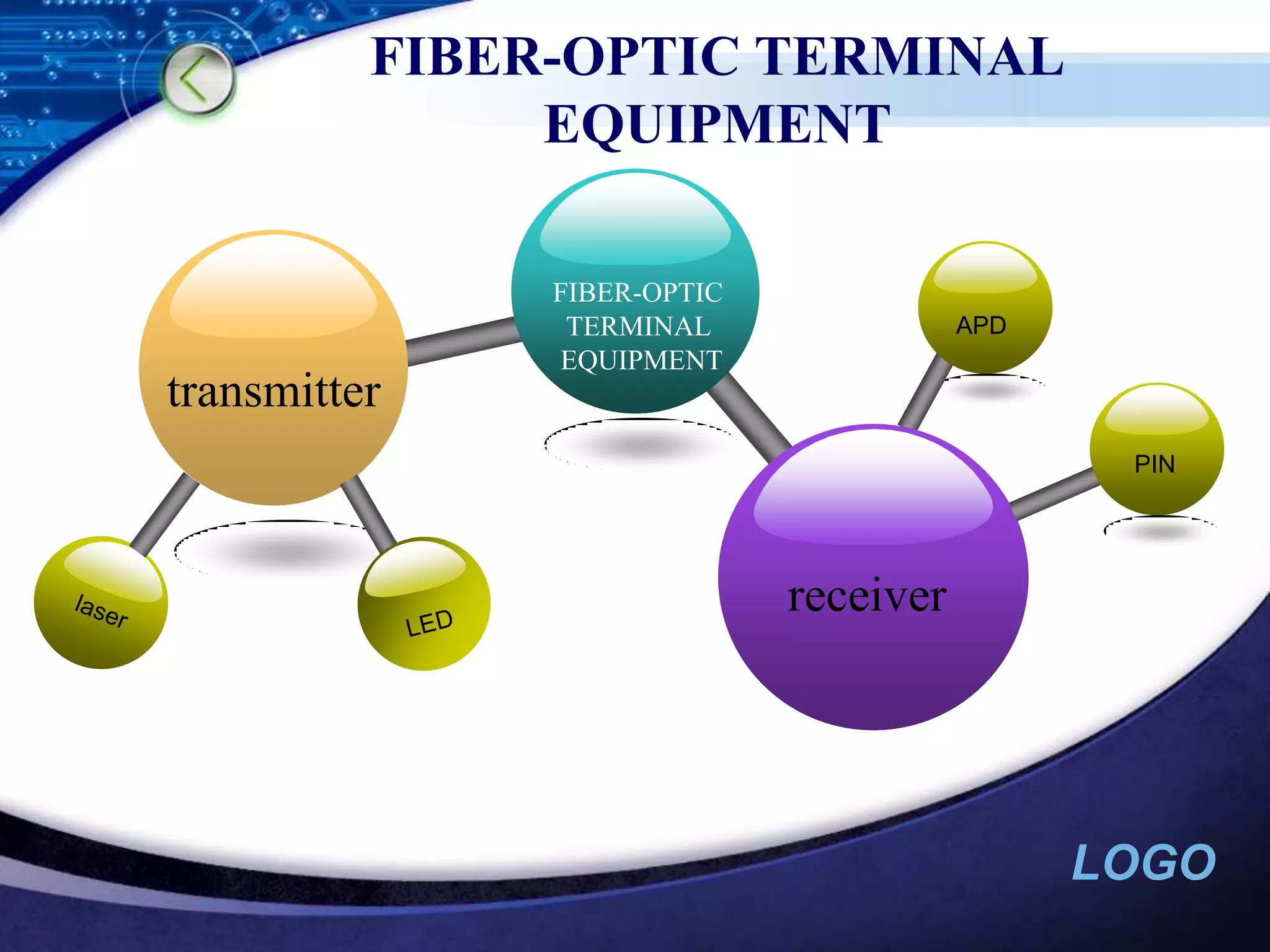
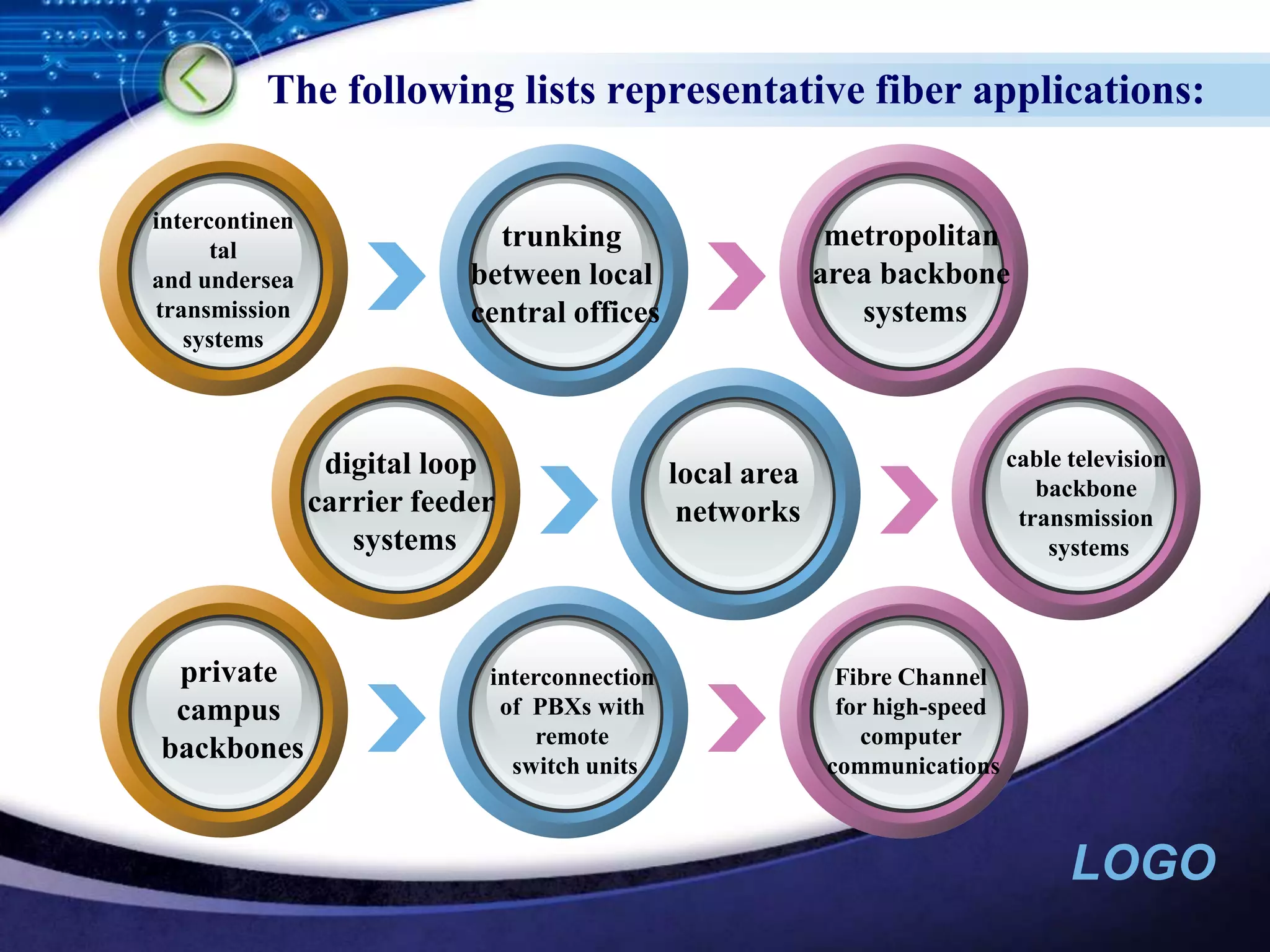
Optical networking uses fiber optic cables to transmit digital signals through pulsing light. There are different types of light sources (such as LEDs and lasers) and fibers (single-mode and multimode) that are used depending on the distance and bandwidth needs. Optical networking has applications in both private networks like campuses as well as public networks for long-distance transmission, cable TV backbones, and connecting devices like PBXs and switches.